Cloud Computing trends and predictions
As a cloud-based world grows closer and technology continues its rapid evolution, companies need to not only understand but also strategically navigate the complexities of the cloud computing industry to remain competitive and innovative in their respective markets.
Introduction: Riding the wave of Cloud Computing trends
According to Accenture, a global information technology company, “since 2010, the global cloud services industry has risen year after year to reach a $370 billion valuation in 2020, marking a growth of over 380 percent in ten short years.”
Part of this rise can be attributed to the effects of the global pandemic because COVID-19 has facilitated a focus on cloud capabilities as companies compete to thrive in an increasingly remote working era. The use of the cloud has become an essential part of a firm’s tech stack and is crucial to business success.
As a cloud-based world grows closer, companies need to understand the cloud computing industry. There are various latest cloud computing trends and predictions in the industry that must be catalogued to ensure that companies can see future growth.
These are, among others, hybrid cloud environments, the “as a service” model, cloud managed services, cloud automation, cloud gaming and artificial intelligence.
Cloud trend #1: The rise of Hybrid Cloud Environments
There are three approaches to implementing cloud solutions: public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud.
In a public cloud environment, cloud computing resources are shared across multiple organisations, and the infrastructure is managed by a third-party service provider.
In a private cloud environment, a single entity or organisation owns and manages cloud infrastructure. Therefore, private resources are hidden behind a firewall or other security measures.

Many cloud consultants who help organisations learn how to conduct cloud migration the right way advise a balance between public and private cloud environments, because relying solely on public cloud technology is not secure, and relying solely on the private cloud is far too expensive.
Therefore, hybrid cloud is in high demand. The top cloud firm, AWS, and its competitors, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and IBM Cloud, are expanding their development of hybrid models and cloud consulting services that adopt both public and private cloud architectures.
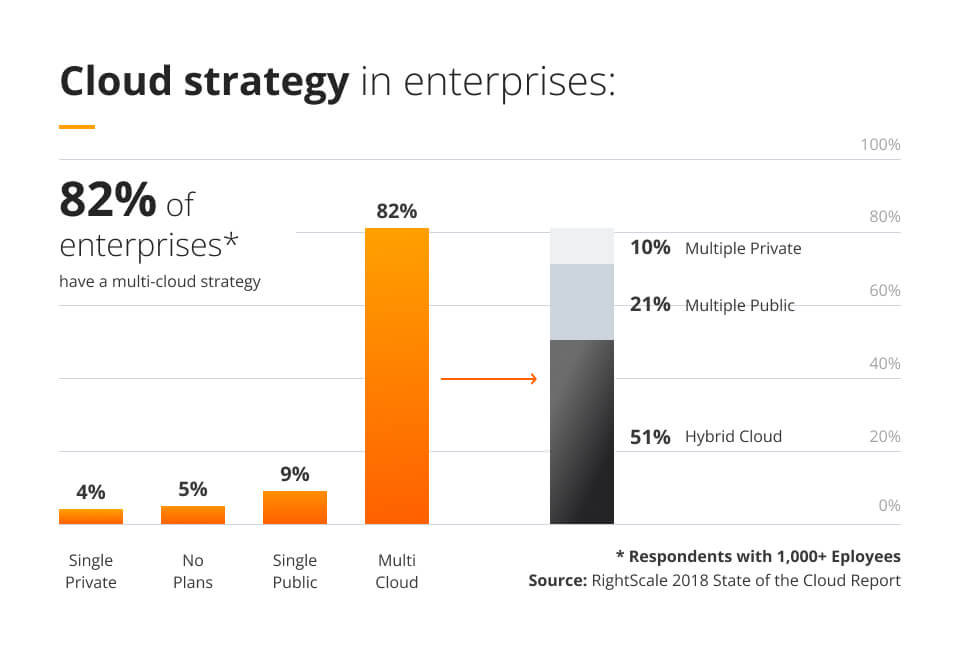
A hybrid cloud environment is a flexible infrastructure created using key features from both public and private cloud services. The graphic below shows that 51% of enterprise clients use a hybrid cloud environment in their multi-cloud strategy. A hybrid cloud is a cost-effective IT infrastructure that is able to benefit from both the large storage and collaborative capacities of the public cloud and the security of the private cloud.
Optimisation of the right balance between private and public cloud is the main challenge. Still, there are many cloud big data and cloud consulting services that help organisations optimise their resources through data analytics and application integration.
The benefits of a hybrid cloud include superior scalability, cost, control, and speed. Regarding scalability, hybrid cloud solutions use public cloud options to help add more computational power and run more complex and resource-demanding applications.
In the public cloud, a company pays more if they use more. With the development of the hybrid cloud, there is no need to waste time waiting until the organisation can afford to buy more servers. The company can simply use the resources provided by the cloud service.
Regarding cost, companies can save money during the growth process due to off-site storage with public cloud computing. On the other hand, the private section of the hybrid cloud is used to store crucial information. Therefore, an organisation reduces the costs of constantly moving between two cloud providers: public and private.
Regarding control, the private cloud segment of the hybrid cloud allows for control over an organisation’s security. A firm can customise its cloud strategy to help adapt to the organisation’s business needs.
Finally, a hybrid cloud solution encourages efficiency and performance. It allows an IT team to optimise the network in ways that reduce latency and simplify the data transfer process. The hybrid cloud can also use edge computing. This enhanced control can save processing time and optimise application operations.
Overall, the future of hybrid cloud services is bright. With a variety of industry leaders producing hybrid cloud services in addition to more cloud-native applications, it is becoming easier for businesses to migrate their resources to the cloud.
Guide for successful cloud adoption
Download our comprehensive ebook for cloud adoption
Cloud trend #2: Edge Computing
Edge is a new way of computing that aims to process data nearer to where it originates, usually at the user or device that’s creating the data. It helps save bandwidth and minimise the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to a central point.
The main goal is to decrease response time, enhance processing efficiency, handle bigger data sets, and produce immediate practical insights.
Using edge computing has various advantages, such as providing better user experiences by giving more relevant and accurate predictions. It also boosts data privacy since it processes sensitive data locally, minimising the need for data transmission to far-off cloud servers.
Additionally, edge computing can deliver real-time responsiveness in applications like self-driving cars and telesurgery, where quick decisions are crucial.
However, edge computing doesn’t operate in isolation; it collaborates with technologies like 5G, IoT, containers, service and data mesh, software-defined networking, and digital twins.
These synergies amplify edge computing’s efficiency, reliability, and manageability, facilitating autonomous decision-making and real-time processing.
Cloud trend #3: Cloud security and resilience
Security is becoming increasingly important as more organisations move their workloads to the cloud. Maintaining consistent security across multiple platforms is crucial especially in hybrid and multi-cloud infrastructure. There are several strategies that businesses can consider to achieve this.
Utilising cloud-native tools and automation can help quickly identify and counter threats. Additionally, implementing encryption, multi-factor authentication, regular cloud audits, redundancy, failover mechanisms, and disaster recovery plans can protect against unauthorised access, breaches, and cyber threats. These measures foster trust in the cloud ecosystem and ensure uninterrupted service availability.
The Cybersecurity Mesh is a new approach to security that prioritises the identity of users and devices over traditional network boundaries. This recognises the need for security to adapt to modern work environments, providing strong protection no matter where users and devices are located.
The Zero Trust model complements this by questioning the idea of inherent trust within networks, requiring strict verification for all entities seeking access to resources. By treating everything as potentially untrusted, this model establishes a strong security posture that is crucial in today’s complex threat landscape.
Educating organisations on common threats such as misconfigurations and unauthorised access is also important. Rigorous scrutiny of third-party providers is necessary to safeguard against supply chain attacks. By implementing these measures, businesses can ensure the safety and security of their cloud environment.
Cloud trend #4: Cloud as a Service
One of the most significant trends in cloud computing is the “as a service” model. “As a service” is a term that is used to describe a type of business model in which customers can access and use software applications or services on a pay-as-you-go basis.
This type of arrangement gives customers the flexibility to use a given offering as they need with various degrees of managed services and staff augmentation rather than paying a fixed cost for resources that they will not use and do not want to commit to long-term.
XaaS has presented itself as an affordable option for accessing crucial digital resources and, as a result, has seen exponential market growth. According to Fortune Business Insights, “the global everything as a service market size is projected to reach USD 2378.07 billion in 2029, at a CAGR of 23.4% during the forecast period.”
Perhaps the most significant benefit of the as-a-service model is cost efficiency.
The pay-as-you-go concept has revolutionised the industry approach with regard to avoiding peripheral costs related to purchasing/producing, maintaining, and licensing traditional software. The scale that as-a-service providers operate on makes these support costs nearly negligible, allowing them to pass on savings to their customers.
Additionally, as-a-service models often facilitate the ability to find unique and customised software development that is not available through traditional means.
Top Cloud providers specialising in a particular offering can help ensure maximum efficiency and quality for each aspect of a company’s digital space rather than the company spreading its resources thinly to achieve subpar results across a wide area.
This aspect can be an important advantage for businesses that require specialised functionality that they may not be able to achieve with a generally-oriented tech team.
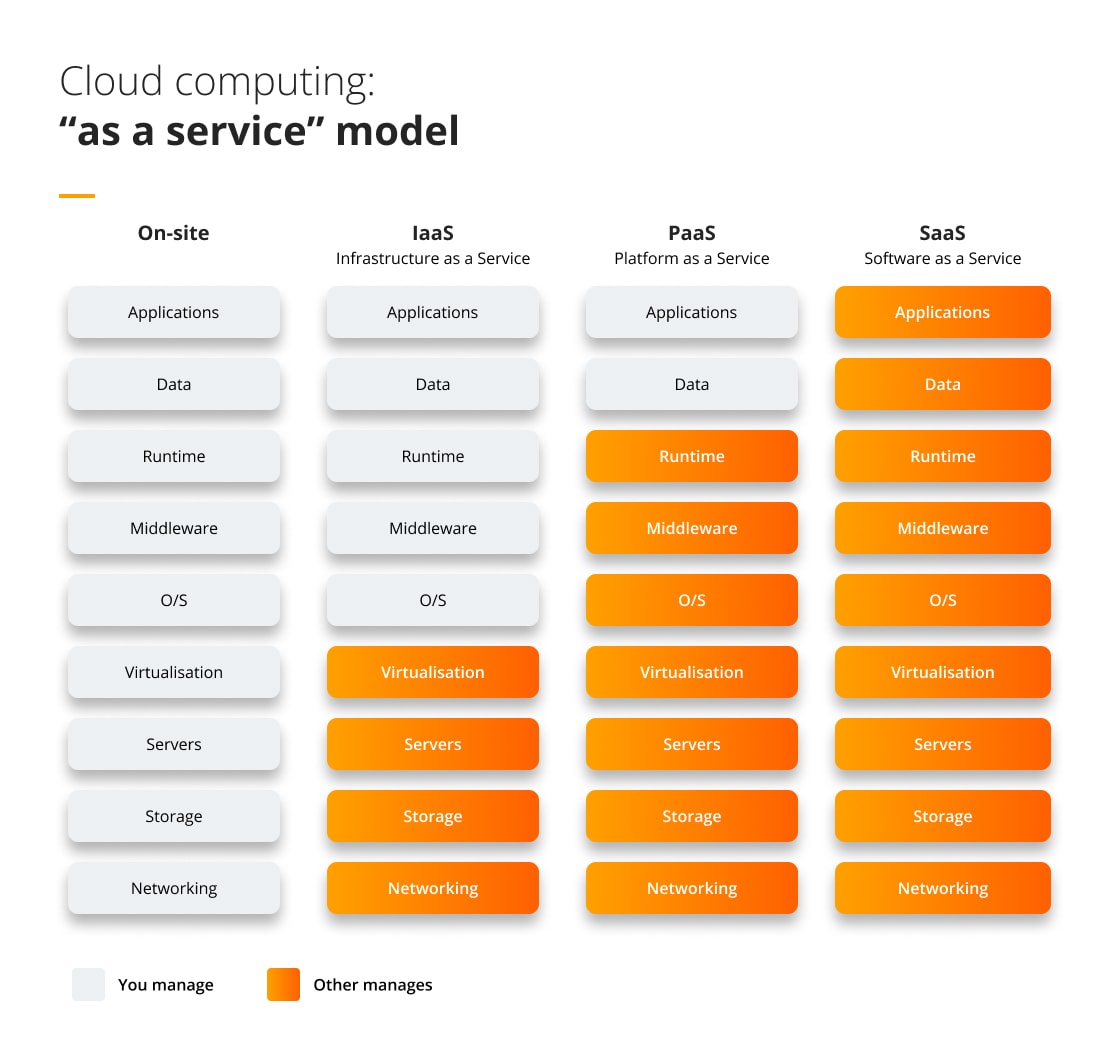
TYPES OF XAAS
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud-based software distribution model that consists of a provider hosting applications and granting access to customers, typically through a subscription payment. In the SaaS model, customers expect that the provider manages everything needed by them. This expectation means that the barrier to entry for SaaS offerings and development is extremely low, making them optimal for small businesses with little tech know-how or large firms that do not want to allocate resources to specialised projects. These services often include web development and design, custom software development, UI design, or app development. Competition between an ever-growing number of SaaS companies has resulted in a vast array of inexpensive solutions that are guaranteed to provide value for your business, regardless of size.
Platform as a service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model that provides users with a platform for developing, running, and managing applications. PaaS typically includes both the hardware and software designed to work with your business to implement application development, application testing, and application deployment, making it a complete solution for enterprises looking to transition their applications to the cloud. PaaS providers often offer a variety of services, including storage, networking, and databases, making it easy for organisations to find the right cloud service provider that will build and deploy complex applications.
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is a cloud computing model that delivers servers, storage, networking, and data centre space infrastructure. Rather than providing a comprehensive solution, IaaS providers simply allow firms to host their digital operations and technology in their space rather than hosting them in expensive and inefficient in-house data centres. IaaS providers typically charge based on metered usage, making it a cost-effective solution for businesses that need to scale their infrastructure up or down on demand. IaaS can be used to deploy and manage workloads in the cloud or to supplement an existing on-premises infrastructure. In either case, it can help businesses to reduce their capital and operational expenses.
If you want to know more about the benefits and the best use of each type of cloud, take a look at:
Cloud-based software development: benefits and solutions your business needs
Which cloud architecture model is best for security?
Why is Cloud Computing important and will get even more vital in the future?
Cloud trend #5: Cloud Automation
Cloud automation has become employed more frequently by enterprises as a means of optimisation of management of their cloud environments due to the difficulty in maintaining a multi-cloud approach. For example, cloud-agnostic tools like Terraform allow organisations to develop identical infrastructure across all platforms.
Soon, functions like dashboards could allow for the use of such tools and greater solutions for digital transformation strategy, as the ability to view all splintered cloud services in one window would be incredibly useful.
These functions would also allow for more opportunities for machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) implementation because it would steer developers towards future possibilities in their industries and improve their skills.
Especially for multi-cloud or hybrid cloud, organisations want analytics to help them compare different metrics of cloud performances. Operating without an understanding of efficiency also makes an organisation more vulnerable to threats.
Leveraging machine learning capabilities can create more contingency data for an organisation, creating better threat preparation.
Cloud trend #6: Cloud and AI
Cloud computing technology and AI have a symbiotic relationship. While AI powers cloud computing – managing data, revealing insights, and optimising workflows – cloud computing increases its impact and scope.
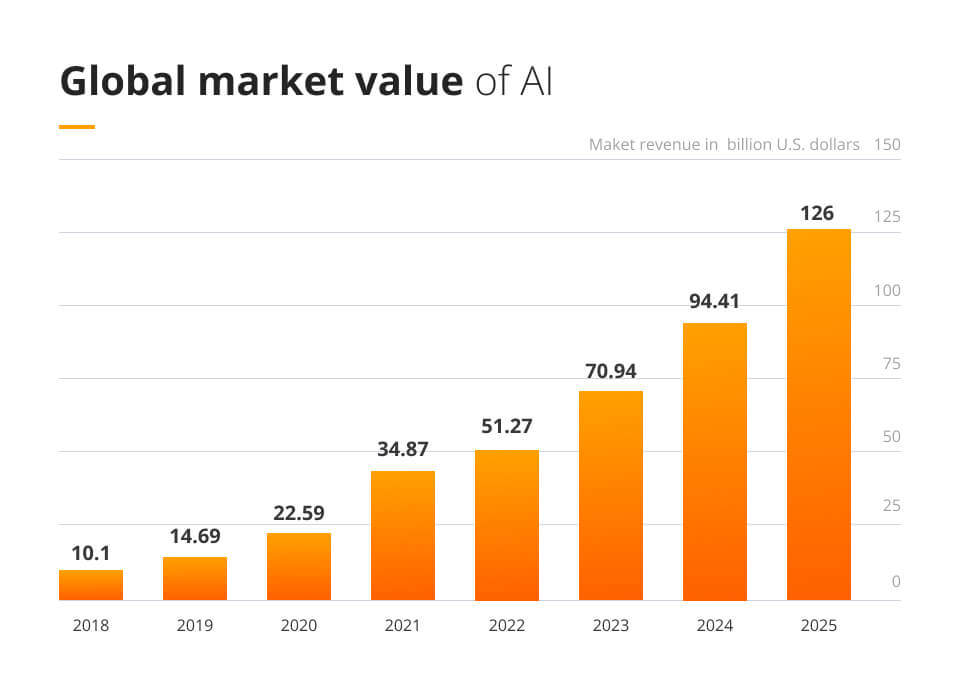
Statista states, “by 2025, the global market value of AI is estimated to surpass $126 billion annually” meaning that businesses not taking advantage can fall behind their competition quickly.
Cloud services make AI accessible to organisations who struggle to enter an industry with high requirements. Traditionally, investing in AI technology requires top technical skills, computing power, as well as a large amount of capital needed to invest.
However, with cloud services offering AI to their customers, companies are able to benefit from AI without making a sizable upfront investment.
Businesses get the most out of AI and cloud when they combine both. Cloud solutions remove the need for expensive on-prem IT services, facilitating easier data recovery with constant backups. While this occurs, AI can utilise the cloud to gain insights and implement measures throughout the system after learning.
When both work harmoniously, a company’s business analytics, IT services, and data insights can all go the extra mile, leading to better innovation, digital product design, and collaboration, among others.
Cloud trend #7: Disaster Recovery Cloud Computing
The practice of using cloud services to restore vital IT systems, applications, and data following disasters is called Cloud DR.
One common approach is DRaaS, where cloud providers manage data replication, storage, and recovery process orchestration. Cloud DR has several advantages, such as business continuity, scalability, cost efficiency, automation, and different recovery options.
There are significant differences to consider when comparing Cloud DR to traditional disaster recovery methods. Traditional approaches often require maintaining secondary data centres, which can be complicated and costly.
However, cloud disaster recovery eliminates the need for separate physical recovery sites by using cloud resources for backup. The cloud’s flexibility enables faster recovery times and eliminates the need for significant physical infrastructure investments.
Cloud trend #8: The Green Cloud
“Green Cloud” means using cloud computing to reduce the impact of IT on the environment. In a broader context, Green Computing, also known as Green IT, encompasses a strategy that prioritises efficient resource utilisation to lower the carbon footprint of computing.
To achieve that, businesses optimise data storage, minimise hardware requirements, and adopt ecologically conscious practices throughout the lifespan of IT equipment. Benefits include fewer data centres, remote work and less resource consumption.
How to stay ahead: preparing for the future of Cloud Computing
Remember that cloud computing predictions and development directions are dynamic and constantly evolving. Flexibility, a willingness to learn, and the ability to adapt to changing trends will be crucial for organisations looking to leverage the benefits of cloud computing effectively.
Here is how you can prepare for the future:
Skill development: As businesses increasingly depend on AI-driven insights, it will be crucial to have skills in data analysis, machine learning algorithms, and ML & AI PoC development. Start investing in training ahead of the curve.
Architectural transformation: Discover the advantages of incorporating cloud computing into your applications. Additionally, consider exploring the potential benefits of implementing a serverless architecture for your applications. Utilizing serverless platforms can free up your time and resources, allowing you to focus on enhancing your application’s functionality rather than infrastructure management.
Security and compliance: Becoming familiar with Security Access Service Edge (SASE) technology is important. With remote work becoming more common and cyber security being a top priority, incorporating SASE principles into your network architecture can significantly improve your organisation’s operations.
Investing in resources: Remember to allocate resources for research and experimentation with new technologies. One approach is to create a sandbox environment where your team can safely explore and test emerging top cloud computing trends.
Collaboration and knowledge sharing: Encourage your team members to collaborate with each other and share their insights. Suggest attending workshops, online courses, and conferences focusing on cloud computing trends.
Demystifying Cloud Adoption: Embracing Cloud Services
Agility and change are necessary for cloud computing companies to become more efficient and successful. These different trends will grow faster as the adoption of cloud computing services increases, allowing for better insights to be derived from the industry.
Hybrid cloud migration, the “as a service” model, cloud automation, artificial intelligence are all crucial developments in the cloud computing industry, and providers that implement these trends will be able to provide higher quality cloud technology to their consumers.
Tracking and unpacking these predictions will ensure that any business grows to new heights due to recognising the changes and key aspects of the industry. As the world continues to embrace cloud services, such recognition will prove essential to sustained growth in next years.