How does artificial intelligence work?
Artificial intelligence is the simulation of human intellect in machines that are programmed to mimic humans by thinking like us.
AI and its offshoot, machine learning, will be a foundational tool for creating social good as well as business success.Mark Hurd
Artificial intelligence defined
Artificial intelligence is the simulation of human intellect in machines that are programmed to mimic humans by thinking like us. It is related to traits which have traditionally been associated with the human mind, such as learning and problem-solving, and is focused on rationalising and selecting the correct course of action to achieve a specific goal.
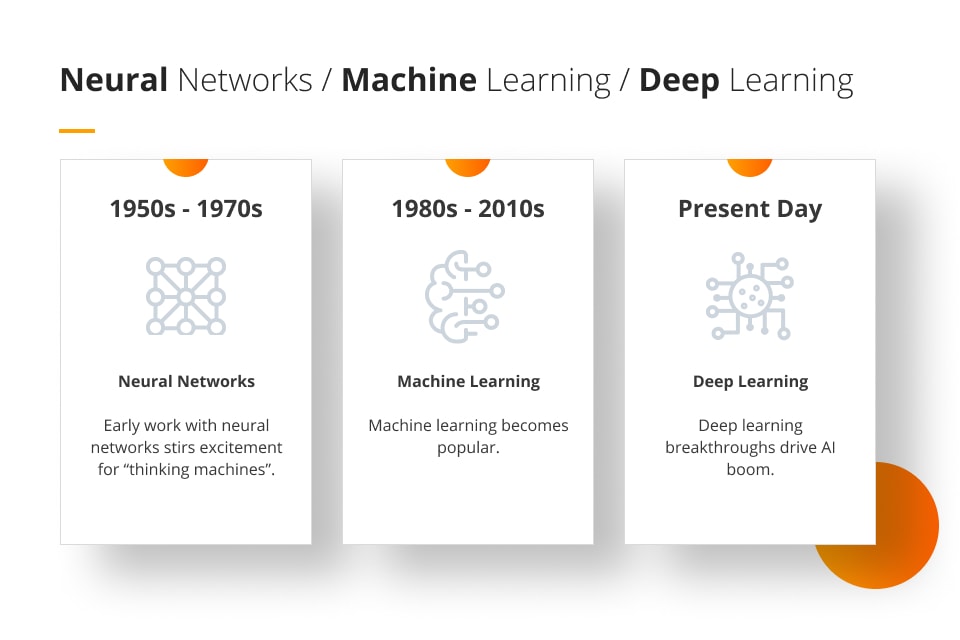
A subcategory of artificial intelligence is machine learning. This is the notion that machines not only can carry out tasks, but they can “learn” information based on data and previous operations, and make the appropriate adaptations without human assistance. Deep learning techniques are used by AI tools provide the framework for machine learning, by processing and absorbing huge amounts of data in the form of text, video and images.
A brief history
“Artificial intelligence” as a term was coined in 1956. Early 1950s research explored topics to do with problem-solving, and by the 1960s, the Department of Defence in the USA took a closer interest in the topic and began experimenting with basic AI and replicating basic human reasoning. DARPA (the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency in the US) began using AI intelligence in the 1970s, later managing to create smart virtual assistants in 2003, long before Siri or Alexa. This early research paved the way for the modern AI tech that we see around us today.
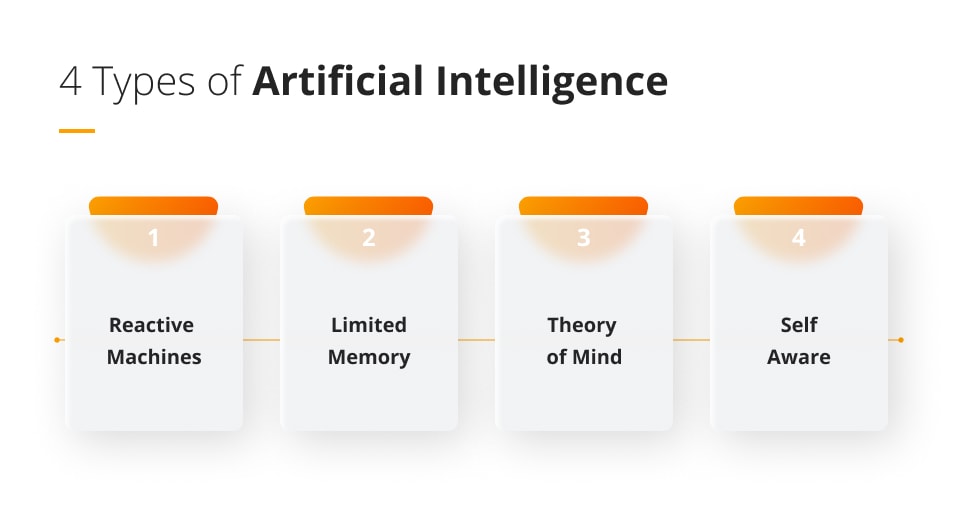
Four types of approaches
Artificial intelligence can be categorised into four main approaches, which are loosely based on Maslow’s hierarchy of needs.
These are:
Reactive machines
This is the first iteration of any AI system. Reactive machines can only perform basic functions and no actual “learning” occurs. It deals only with reacting to input and offering some limited output. It has the simplest architecture and is readily available across the web, meaning they can easily be obtained and used. The reactive machine cannot store any input and it cannot learn.
An example of a reactive machine is IBM’s chess-playing computer, Deep Blue. It can only analyse the opposing player’s input which, when completed, prompts it to calculate the best possible move by predicting all possible outcomes.
Limited memory
This is the second iteration of AI technology. Unlike reactive machines, these are able to store data and previous predictions and use that information to make calculations, forecasts and further predictions. These limited memory machines are more complex in that they require a limited memory to be created, but they can then get implemented as a reactive machine.
There are three main types of machine learning models that can be used to attain the limited memory framework:
- Reinforcement learning: These make predictions through trial and error.
- Long short-term memory (LSTMs): These help predict the next factor in a given sequence by analysing past data (including human input relating to past history) and ranking them by importance.
- Evolutionary generative adversarial networks (E-GAN): This machine evolves at every stage through memorising and learning information, as well as using it to exponentially grow.
The core approach to limited memory AI is that the model is continuously trained on new data and the AI environment is such that the model is automatically developed and renewed with each iteration.
Theory of mind
This third stage of AI development is the current limitation of our expertise. It is the concept that bots and AI technology are able to actually understand human thoughts and emotions and are able to respond to them intimately. At this stage, AI can understand our requests and input, but it has no concept of our emotions.
If you ask Siri a question while sobbing or screaming, it may technically answer your question, but it will not have the capacity to recognise your emotional distress and offer you advice. Theory of mind AI systems will, in theory, be able to do this and will be a better “companion”.
Self-awareness
This is the final iteration of AI development, Class III, and will not be achieved until long in the future. It is based on the concept of AI becoming self-aware and sentient. It would far surpass the ability to understand human emotions, and would actually be able to create other AI machines with the same level of awareness. Right now, it only exists in stories and science fiction, but it could well be a very real possibility in our not-too-distant future.
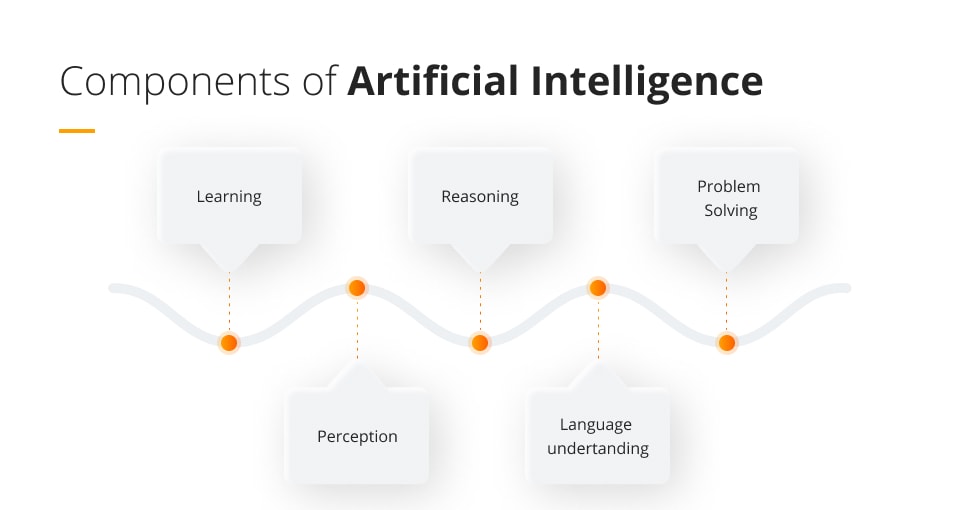
What are the basic components of artificial intelligence?
In order to understand AI and how it can be used by companies and individuals to carry out a range of tasks much more efficiently than any human could, it is important to fully understand the five main components of AI.
Learning
Learning occurs in AI when the machines involved are able to retain and memorise new material and data. This could include solutions to any given problem, language and lexis, data and so on.
Deep machine learning is able to provide the foundation for accurate predictive analysis through the use of operational data. With this machine learning, the AI system is able to find correlations in data that are hidden and then create predictive models. One such application could be in predicting when a system or physical machine is going to fail or be in need of repair and preemptively ordering new parts or scheduling it for maintenance.
Reasoning
Until recently, the ability to “reason” was exclusively a human trait. Being able to reason allows an AI application to decide on various suggestions or recommendations based on the set of inputs that they have received.
An example of this would be when a virtual assistant is able to recommend a certain type of restaurant based on the questions or input it has received from a human user. It will use reasoning to decide which types of restaurant to recommend, based on the user’s location, preferences and any other information that it was provided. By using either deductive or inductive reasoning, the AI system can draw on relevant inferences from the communication it was provided.
Problem-solving
Problem-solving involves analysing data to find a given solution. This could be based on any amount of data with numerous considerations which would be close to impossible for a human. Solutions are tailor-made to satisfy the given problem, often exploiting the specific features that were provided in the case where the suggested problem is actually embedded. This is known as the “special purpose method”.
Another type of problem-solving situation is known as the “general purpose method”, where it encompasses a range of vivid issues. This offers a much broader solution that could refer to a wider range of issues. The AI system goes through a process of reducing the difference in each step between the given goal and the current state of the system. For example, if you are shopping online for an item but you can’t remember the name, the problem-solving AI application can begin to narrow down your choices based on those aspects you can remember (such as type, price, colour and so on), until, ideally, you find the desired result.
Perception
When humans “perceive” something, we are using our sensory organs to understand the environment around us. AI “perception” does exactly the same. It scans the given environment, either digitally or physically, to learn what it is composed of. This could be through the use of software or components such as sensors, cameras or audio equipment.
An example would be in modern cars, which scan the road around us for hazards, road markings, traffic lights and adverse weather conditions.
Language understanding
Language as we know it is simply a set of signs that refer to various concepts or notions. Language understanding in AI technology has been widely used for a long time already in the form of spellcheck and autocorrect applications. The AI system scans a text or body or writing for errors, mistakes, and inconsistencies, and can make suggestions for improvements.
Another application of language understanding AI is to filter our spam emails. The AI technology scans our inboxes and separates what it considers to be “real” and “junk” messages into different folders through recognition of certain word groups.
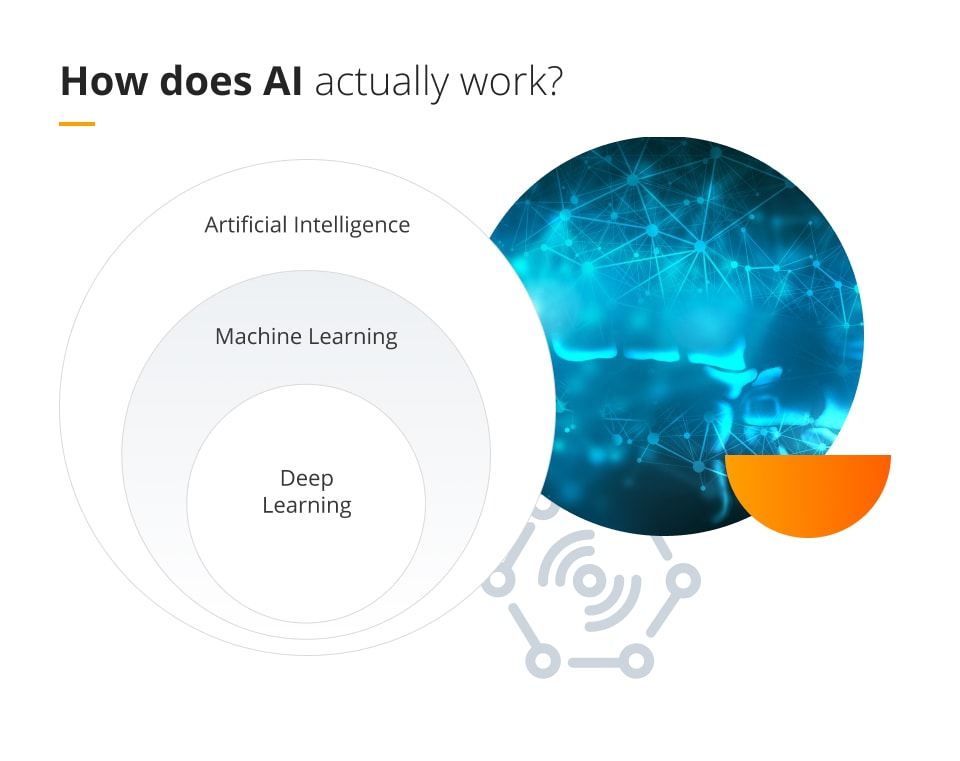
How does AI actually work?
AI works through the combination of large amounts of data with ultra-fast, iterative processing and intelligent algorithms. This allows the AI software to automatically learn from any patterns or features that are found within that data.
There are many subsets to artificial intelligence that help that AI technology to consolidate and consider problems in a human-like manner. As we mentioned at the beginning of the article, the first subset is machine learning, where the AI system looks at both the given and past data, highlights patterns and makes informed decisions autonomously.
A subset of machine learning is deep learning. This is a type of machine learning that requires an enormous amount of data in order for it to form “neural networks” (somewhat akin to how the human brain works). It requires an extremely high amount of processing power for it to be able to compute outputs. Examples of deep learning AI technology include self-driving cars, face and image recognition software, and speech recognition.
As mentioned above, neural networks function like the neurons found inside a human’s brain. They transmit information to one another via “bridges” in its infrastructure, processing the data and forming ever complex connections.
Summary
AI is redefining how we view and work with the world, both in business and in our private lives. Companies are successfully utilising AI technology to improve their operations, increase efficiency and drive down costs. As we progress as a species, it is only logical that the widespread usage of AI technology will only continue, transforming and reshaping the world as we know it.