Human-Centered Design: how empathy and innovation shape IT products
Human-Centered Design is a philosophy that can take your company’s projects and products to a completely new, higher level. In this article we speak about this human face of technology to see why it is key to every IT product’s success.
In today’s digital era, we tend to trust technological advancements no matter what we do. After all, the age of technology calls for advanced solutions, and businesses are focused on delivering them. Yet statistics show that as much as 70% of all projects fail. Why? Because many of them do not take into consideration the needs of end-users. Human-centered design is all about them.
What is Human-Centered Design?
Before we look into the advantages of human-centered design, let’s start with the definition.
Used in design, management, and engineering frameworks, Human-Centered Design is characterised by involving empathy and human perspective in all steps of the design process. From observing the problem and analysing its context through brainstorming possible solutions to developing, early testing, and implementing the products.
The human-centered design was championed by Herbert Simon, Nobel Prize laureate, and later developed and taught by the Stanford University Design School. It is a ground-breaking solution as it allows businesses to look at their problems from the human perspective.
Comparing Human-Centered Design with traditional design approaches
Human-centered approach prioritises people’s experiences, emotions, and behaviours as fundamental to the User-centred software design. By placing the customer at the forefront of the process, this method emphasises the importance of listening to and learning from the customer to address their actual problems.
Adopting such an approach enables designers to prioritise the user’s needs and incorporate empathy and understanding into their work. The ultimate objective is to make users’ lives easier and more fulfilling through thoughtful product design.
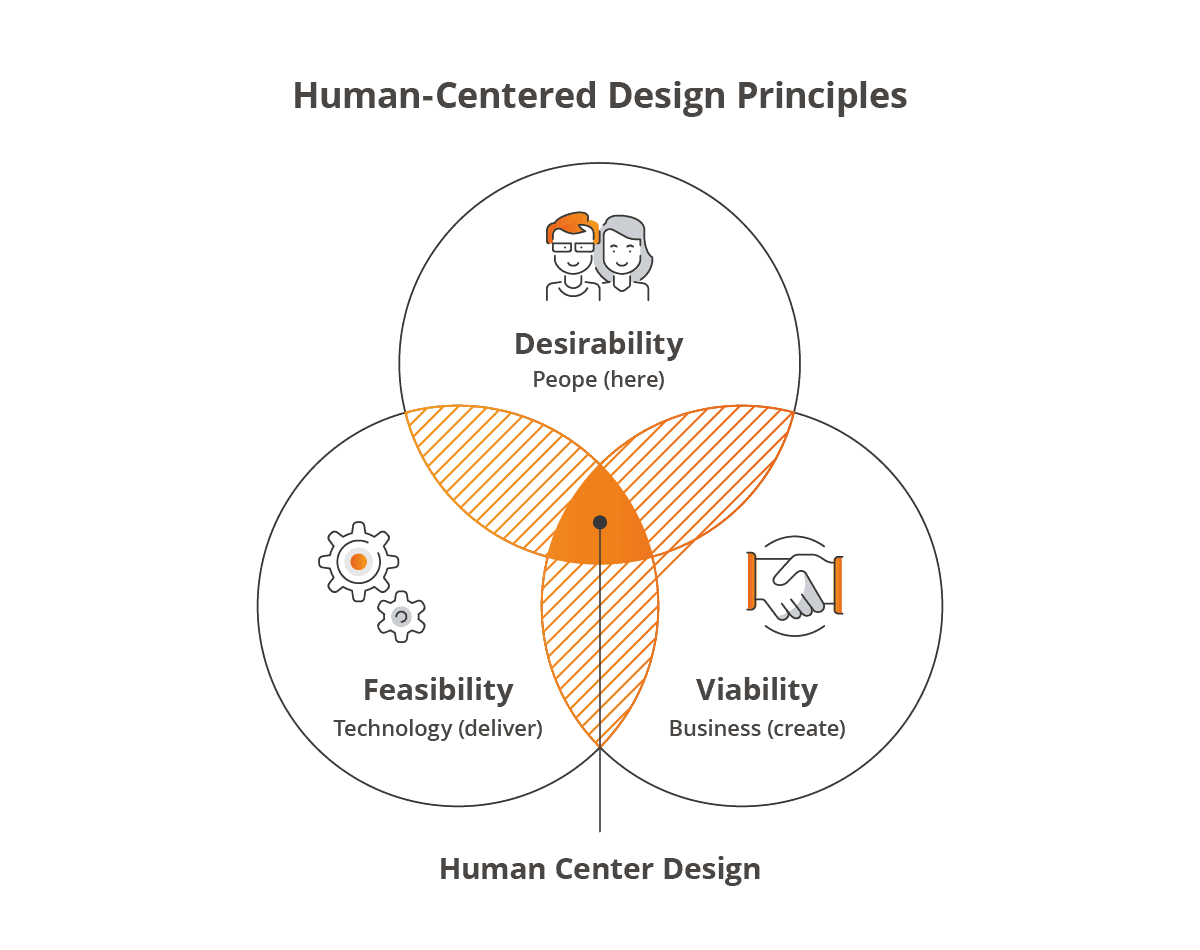
Understanding the principles of Human-Centered Design
The Four Principles of Human-Centered Design provide a comprehensive framework for crafting solutions that are empathetic, effective, and sustainable:
Tackle core challenges: Go beyond symptoms to find real problems. This means looking deeper, even when issues seem simple or obvious.
Focus on people: In our tech-filled world, it’s vital to design systems for people. This includes understanding everyone’s needs and letting inclusivity into tech solutions.
Think big picture: Design with the whole system in mind, not just individual parts. Solutions should work well in the larger framework, benefiting everyone involved.
Iterate and refine: Start with drafts and improve over time. Working with feedback from real users helps refine solutions to be more effective.
Benefits of implementing Human-Centered Design in your organization
User-centered design ensures that products and services truly resonate with their intended audience. Implementing this approach in your organisation not only enhances user satisfaction and engagement but also drives innovation and business success.
How Human-Centered Design enhances User Experience
Human-centered design is a methodology that puts users at the forefront of the creative process. Instead of focusing on creating features, this strategy puts an emphasis on resolving actual issues that people have.
Understanding users, inspiring sympathy, and iteratively improving upon concepts in response to comments are all essential tenets.
Inclusivity in Design: addressing diverse user needs
Human-centered design focuses on creating effective products by emphasising true empathy, user research and collaboration. By involving users in the design process from the beginning, designers can create products that cater to different age groups and levels of expertise.
Integrating feedback: continuous improvement through Human-Centered Design
Continuous improvement of products and services is a methodical process that involves taking feedback from actual users and using it to make better decisions. The idea is that the insights of the end-users can help improve the interactive technology designed for them.
This cycle of continuous user feedback sparks innovation and leads to better products for everyone involved.
Educational perspectives and ethics in Human-Centered Design
Human-centered approach requires designers to be conscious of the potential consequences of their work. The choices they make, which personal biases and perspectives can influence, significantly impact our environments and experiences.
It’s important to balance rapid design methods with deeper introspection and consideration of broader perspectives to ensure ethically sound and comprehensive solutions.
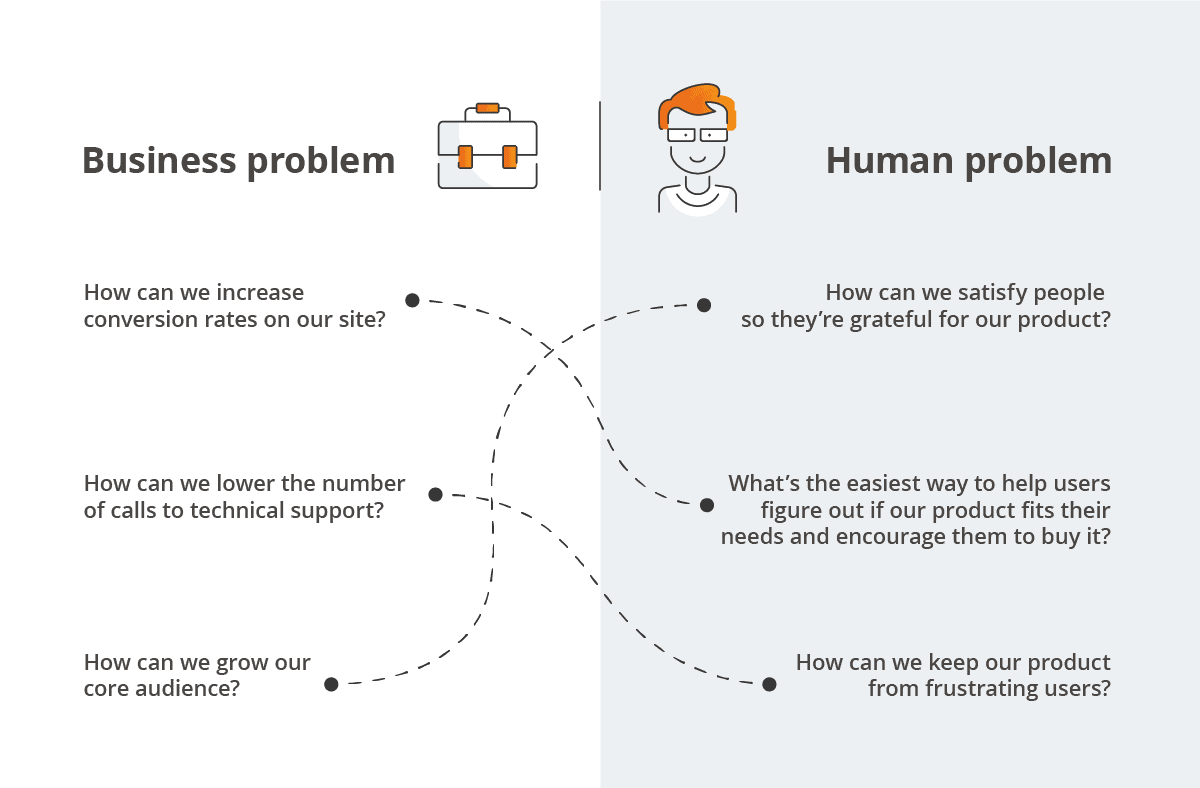
Why is Human-Centered Design key to the success of IT products?
No matter whether you are working on an app or software, your products will always be used by people. It is people that you should have in mind when designing them, not profits, savings or looks, as it used to be done traditionally.
If you fail to consider your customers and don’t engage with them, your products are doomed to fail. In contrast, when you focus on thinking about end-users, you are more open to changes, feedback, and innovative solutions. After all, you are working on products that may possibly improve people’s lives!
Read more about Product Design:
Why is it important to use analysis and design methodologies when building a digital product?
Mockup vs Prototype vs MVP — what’s the difference?
Wireframing in UI/UX design: types, process and tools
A simple guide to the ROI of UX – what is it all about?
How to apply Human-Centered Design principles in the product development process?
When designing IT products, the key is to understand the people who will be using them. Without that, products simply fail.
It is, therefore, crucially important to always ask smart questions and involve end-customer from the very start of the design process so that you can get the right feedback and make changes as the product develops.
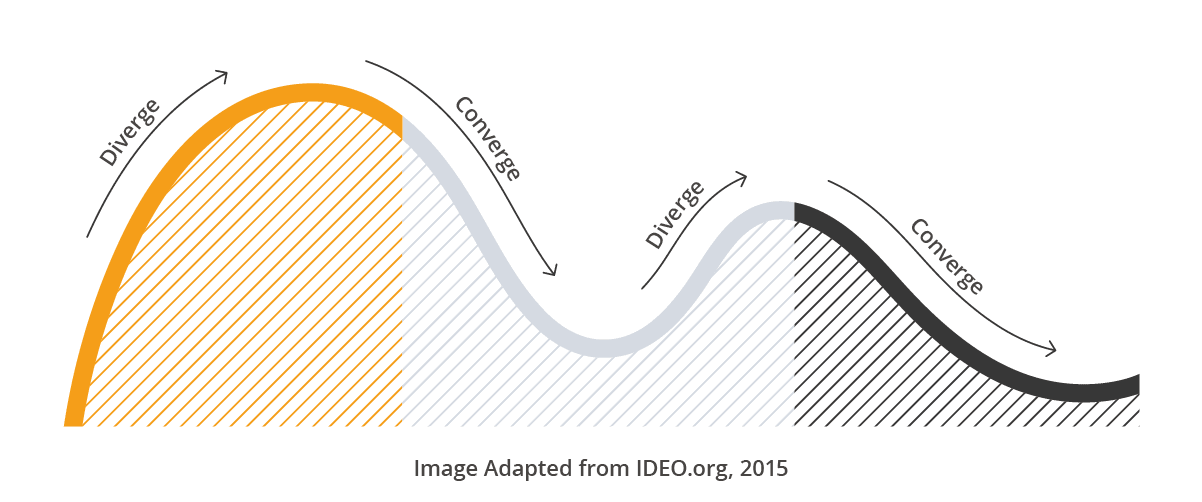
The Human-Centered Design process consists of three phases:
Inspiration is where you need to engage with your target audience to understand their problems, pain points, and what they think may improve their lives.
Ideation means brainstorming on how to address the problem in an innovative way. The golden rule here is that there is no such thing as a bad idea. That’s done; you tweak and change the ideas to come up with a vision for a product that could solve the problem you were thinking about in the first place. This phase is also about creating and testing a prototype on your end-users, ensuring you take all feedback on board.
Implementation, so the time of making the products and marketing them.
Challenges and solutions in applying Human-Centered Design
Applying the human-centered design process comes with its own set of complexities.
Challenges:
Ethics and inclusivity: Maintaining ethical standards and inclusiveness within the human-centered design process.
Balancing objectives: Merging user needs with organisational aspirations.
Complex stakeholder landscape: Dealing with complex problems that involve several parties.
Depth vs. surface: Going beyond solutions that just focus the surface-level user experience in human-computer interaction, and addressing also underlying issues.
Solutions:
User engagement: Consistently involving end-users in every phase of the UX Design Roadmap.
Empathy at the core: Focusing on gaining a thorough understanding of the experience of the end-user.
Cross-sector collaboration: Teaming up with stakeholders from varied backgrounds.
Ethical framework: Incorporating code of ethics into the human-computer interaction design.
Data-driven outcomes: Using evidence to inform design decisions and measure outcomes.
How to implement HCD Principles in your projects?
Once you know HCD is something you want to implement within your organisation, start thinking about the process of doing it. As is the case when introducing an agile framework, implementing HCD in your business may take some time. Start slowly, for example, by using HCD in just one of the products you are developing.
See how it goes – when you test it on a smaller thing, it will be much easier to implement it later across the whole organisation.
At Future Processing, we can help you understand where you are, where you want to get and how to do it. If you are keen to implement human-centered design in your company, a good start may be one of our Digital Product Discovery workshops.
It is where we analyse your business and start asking questions needed to make a change. Want to know more? Get in touch with us to discuss your needs!