The future of cloud security: trends and areas of concern
The security of cloud computing is an area receiving massive emphasis, and rightly so. New trends surrounding the future of cloud security are rapidly emerging, and businesses must stay educated to protect themselves and their customers from growing threats.
Introduction: ascending to the next level of Cloud Security solutions
Cloud computing is steadily being adopted by more and more companies, but the tradeoff that comes with the adoption of cloud computing services is the requirement for high levels of cloud security.
Despite rapid levels of cloud adoption and consequent cloud security improvement, the state of cloud security may not have necessarily improved. According to a 2019 survey by SANS, “unauthorized access of cloud environments or assets by attackers has significantly increased”. This survey found that reported incidents increased to 31% vs 19% in 2017.
Here you can find our complete guide to cloud security management.
But what exactly is the state of cloud security and its future? To determine that, areas undergoing improvement and areas of concern need to be analyzed in how they need to be addressed, and overall trends that outline the current trajectory for cloud security must be evaluated.
Future scope of Cloud Computing Security
Cloud security has grown immensely within organizations following the growth of the cloud computing services industry. Cloud service providers have ensured that security tools will act as cybersecurity for business processes, allowing for significant growth in the cloud environment.
Growth of cloud technologies
Security groups are gaining better experience on how to protect cloud environments from cyberattacks as businesses shift from on-premises technology to future technologies like cloud computing.
Over the past few years, the previous lack of cloud security sophistication is being corrected with on-the-job experience from security incidents and the widespread availability of certifications and training for cloud users and multiple cloud providers.
There has also been a growth in organizations focused on the security oversight of cloud technologies in a bid to ensure confidential computing. Some examples of such groups include the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) and the OWASP Cloud Security Project. These groups aim to provide best practices for securing cloud computing technologies and help identify areas of growth.
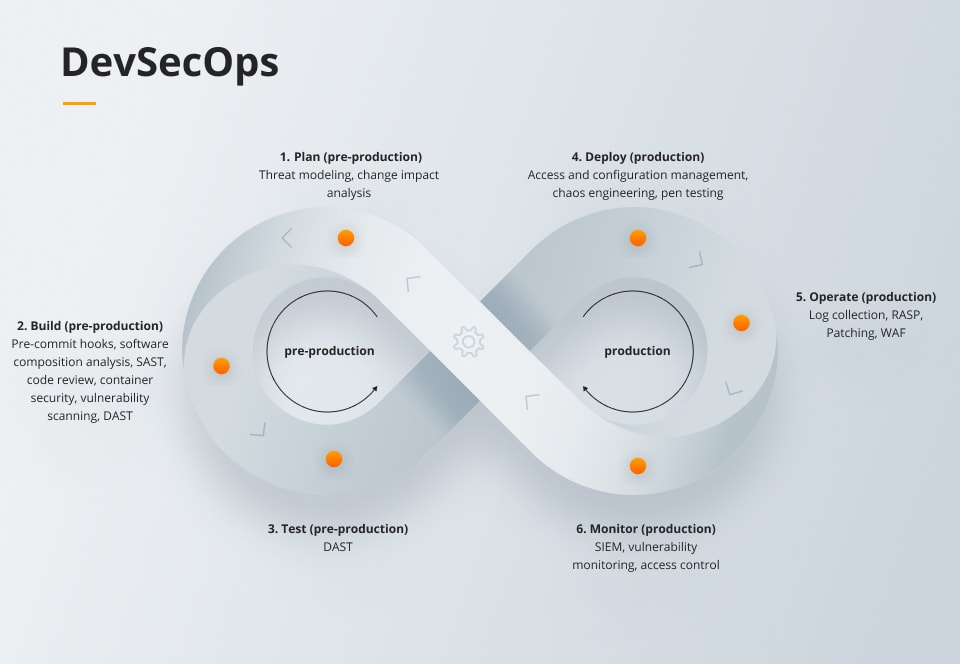
Adoption of DevSecOps
Many companies in the technology industry are adopting DevOps and DevSecOps practices in their attempts at digital transformation.
These practices shift security to the beginning of developmental processes rather than trying to fix everything at the end. By focusing on security earlier in projects, firms can reduce vulnerabilities during software development and deployments and prevent the need for more human intervention in the future.
The automation that typically arrives alongside DevOps practices has also increased security. Using automation when configuring services, users, etc., ensures companies continue to maintain consistency across systems and reduces the risk of misconfiguration.
Tooling and function improvements
The increased centralization of security data has made it easier for most businesses and their security teams to monitor incidents and respond accordingly. Solutions that provide centralization to companies are especially important in hybrid systems and expanding cloud computing deployments. One of them is SIEM – Security information and event management which helps to detect, analyze and respond to security threats before they deal harm to business.
Two particularly useful tools for companies desiring centralization and consistency in the cloud are Security Orchestration, Automation and Response (SOAR) and Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB).
According to KBV Research, “though SOAR technology has only been around a few years, the space is already expected to surpass $2 billion by 2025, expanding at 16% CAGR during the period.” The industry is lucrative because SOAR solutions enable teams to consistently implement security controls, policies, and responses across all systems. By introducing a measure of consistency, teams can increase security by reducing the weak links present within their systems.
CASB are tools or services that interface on-premise and cloud infrastructure. These tools enable the extension of on-premise security tools and policies to necessary cloud technologies, making it easier to secure and monitor traffic in the public cloud environment between on-premise devices and cloud services.
Cloud Security Trends: areas for concern
While there are numerous improvements being made to cloud security, there are still ongoing concerns regarding cloud migration, data privacy and regulatory compliance, and cloud system complexity.
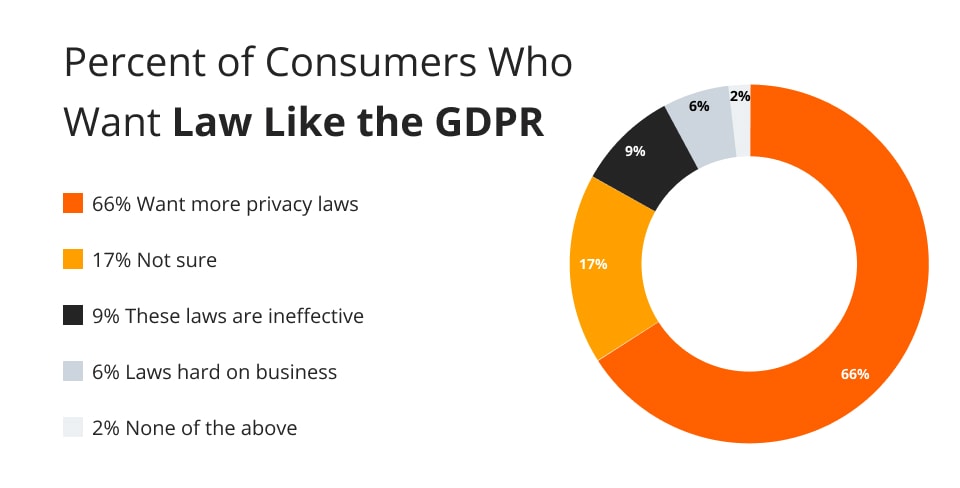
As seen in the chart below, 66% of consumers in the United States would like to see more laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which is enforced within the European Union, come into effect.
Therefore, the number and specifications of compliance regulations are constantly expanding with in-depth requirements and oftentimes harsh consequences.
A major issue that organizations face is the lack of an effective cloud migration strategy. Therefore, their data is subject to the careless transfer of data, a misunderstanding of shared security responsibilities, and misconfiguration.
Data privacy and regulatory compliance
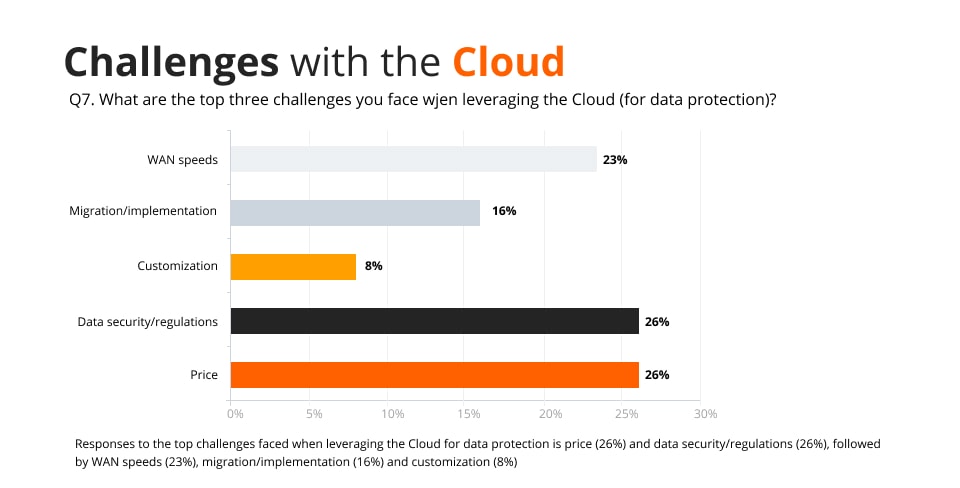
As seen in the graph below, data security and regulations are among the most prominent challenges with the cloud and security.
Currently, cloud providers meet most regulations. However, there is a gap that leaves organizations responsible for filling by making sure all regulations are followed. Therefore, companies need to integrate policies and utilize effective tools to fill this need. One problem is that complying with various regulations can be costly and even require custom configuration.
An alternative to complying with every single regulation is using a hybrid environment to retain regulated on-premise data.
Cloud platforms complexity
Another problem with cloud security is that cloud systems can be particularly complex to secure. While hybrid systems can be used as an effective way to maintain security, the hybrid cloud is the most complex.
Data loss/leakage
Similar to the careless transfer of data, the collaborative power of the cloud paves way for data loss and leakage. According to Check Point, a cloud services company, 69% of organizations view data loss and leakage as their greatest cloud security concern.
In order to ensure no data is lost or leaked, many organizations should be cautious when sharing public links or setting up a cloud-based repository to public. Furthermore, there are tools that can specifically search the internet for unsecured cloud deployments that cause a majority of data losses and leakages across organizations.
Accidental exposure of private documents and credentials
With the growth of cloud-based email and document-sharing services, employees have become accustomed to clicking on links in their emails. However, this occurrence has paved the way for countless phishing attacks. With a successful phishing attack, a hacker could gain access to an employee’s credentials for cloud services.
According to Check Point, 44% of organizations view accidental exposure of cloud credentials as a major concern. After all, malfeasants can compromise the security of cloud-based applications and the other resources the organization has.
It is also crucial to verify confidential vs shared data settings on cloud. Simple misconfiguration of visibility can expose private data to the Internet or external cyber attacks.
Incident response
Even though many businesses have methods in place for responding to cybersecurity incidents, there is a concern that cloud infrastructure brings to incident response. A company has limited visibility and ownership of its infrastructure in a cloud-based environment.
Therefore, traditional incident response methods are ineffective. Overall, incident response in the cloud is tough and should be considered before migrating a company’s resources to the cloud.
With connection to centralization of data it also increases the chances for security related incidents which is why the Security Operations Center (SOC) came to be – to include people, processes and technologies responsible for organization’s information security.
This function, due to required skill set and tooling comes with hefty price, in many cases it’s more efficient to look for a service provider instead omitting it at all.
Predictions and trends in Cloud Security
Various general trends surrounding cloud security define the industry and are critical to understanding the protection of sensitive data. Being aware of these cloud security trends can help businesses decide where to best allocate their resources to stay ahead of the competition.
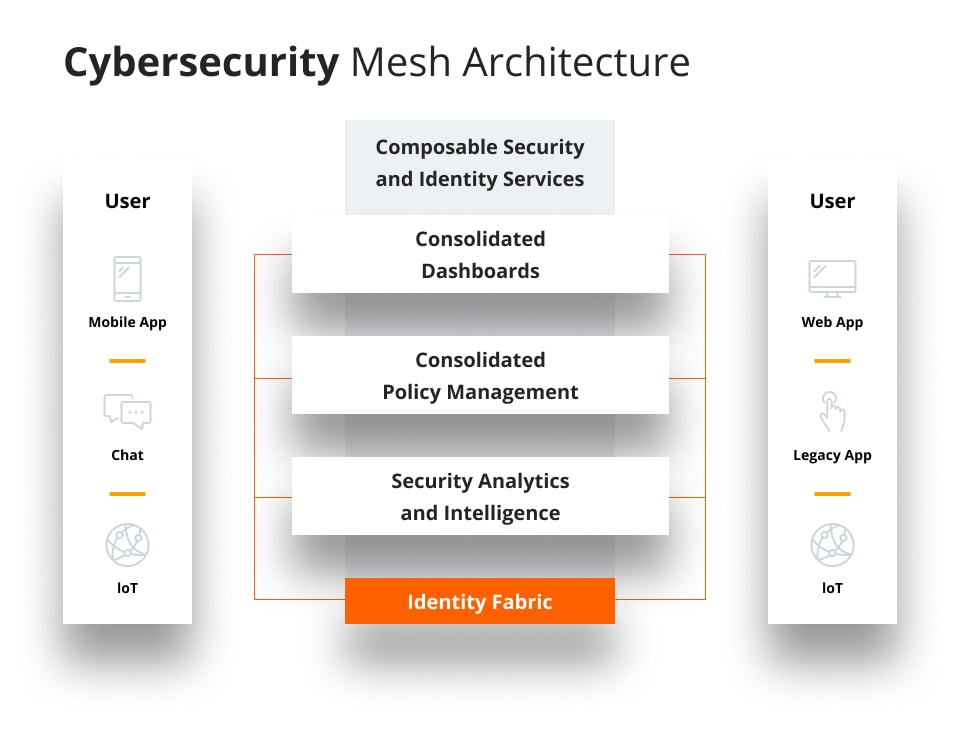
Cybersecurity mesh
Cybersecurity mesh refers to a network of interconnected systems that work together to protect data and infrastructure from cyber threats. Unlike more traditional approaches to cybersecurity, mesh networks take a distributed approach.
This means that rather than trying to protect network infrastructure from a single point of entry, mesh networks distribute the responsibility for securing information across multiple nodes.
By using mesh networking principles, organizations can ensure that no single point of failure can compromise their entire system, decreasing the risk of security breaches considerably. Additionally, mesh network topologies allow for robust encryption schemes and decentralized monitoring and analysis capabilities, further increasing the overall resilience of this cloud technology.
Penetration testing as a service
Penetration testing solutions is a well-known product. However, utilization of penetration testers as a service is a hyping technology in recent years. Utilization of SaaS platforms with combination of DevOps techniques, real pentesters, automation and integration with API provide real-time platform for scheduling, execution and visibility of security tests.
AI and automation
Using scanning, controls and organization risk for identification of exposure companies have is not enough. The amount of data started to create prioritization problems – what to focus on in the first place.
Exposure Management is a process allowing companies to evaluate its external and internal threats and with help of automation, data management and AI focus on the biggest threat (one with the highest attack surface/likelihood of exploitation/biggest risk).
SASE framework
The Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) framework combines a wide range of security measures and technologies, including anti-malware detection and deployment, network segmentation and isolation, multi-vector authentication, certificate-based encryption key management systems, and much more.
Thanks to its extensive suite of features and capabilities, the SASE framework is able to provide strong protections in the most challenging cyber environments. And as more businesses turn to cloud solutions to power their operations in an era based around digital transformation, this framework will become increasingly vital for keeping sensitive data secure from threat actors.
The incorporation of software as a service, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and other cloud native technologies into cloud security through SASE has left a major impact on cloud security predictions. In fact, one of the core capabilities of SASE, zero trust, is becoming an trending topic in cloud security in and of itself for businesses conducting cloud adoption.
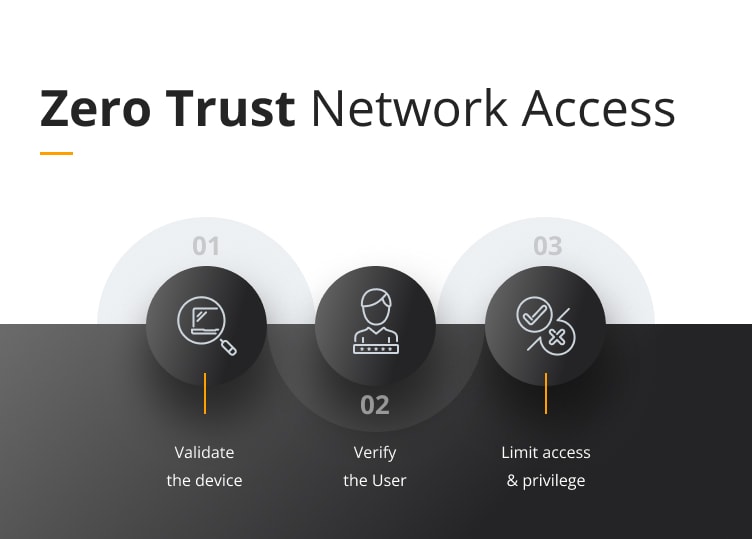
Zero Trust Network Access (Zero Trust Architecture)
A zero trust network model is a modern approach to data protection that focuses on preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information or data breaches.
This method of network security proactively identifies and manages security risks and potential threats, drawing on advanced analytics and cloud architecture to create a more secure environment.
Furthermore, it has become an integral part of the future of cloud security.
By dynamically regulating trust levels in real-time, zero trust helps to ensure that only authorized users can gain access to sensitive data. With this added layer of security, organizations can better protect their critical data from cyber threats and prevent costly breaches.
Whether businesses are implementing this model for the first time or seeking to enhance their existing strategy further, zero trust is an important tool for protecting your organization against malicious threats.
As cloud security technologies continues to develop, future trends will become more and more significant and important for businesses undertaking the cloud adoption process to be educated on.
Every day, more future trends like quantum computing, multi-cloud approach and various advanced SaaS solutions are already becoming a reality.
To stay on the cutting edge of cloud development, most organisations must remain aware of the state of the industry and have the ability to learn and grow based on where the future of cloud security is heading.
Edge Computing: reshaping how data is secured outside centralized clouds
Peter Levine, a general partner at Andreessen Horowitz, thinks that edge computing is the future of data-storage. Smart devices, like autonomous cars, will become ‘tiny’ clouds on their own, thanks to having the computing power of hundreds of PCs. They will, therefore, be able to perform all crucial operations on their own.
The other reason why this course of events seems so obvious for Levine, is the fact that keeping up the bandwidth for those multiple devices would be almost impossible.
That’s why smart devices will only send the most crucial data to the cloud for analysis. The results of this analysis may then be fed back to the devices, allowing them to learn from each other.
The future of network security is in the cloud
Cloud security has risen in importance to business operations over the last half-decade.
The top cloud security trends seem to demonstrate a growing level of competence distributed throughout the industry, which will only lead to an increase in the adoption of cloud tools by organizations.