The future of predictive maintenance
In this article, we explore how augmented reality (AR) and cloud computing are transforming the future of predictive maintenance.
Introduction
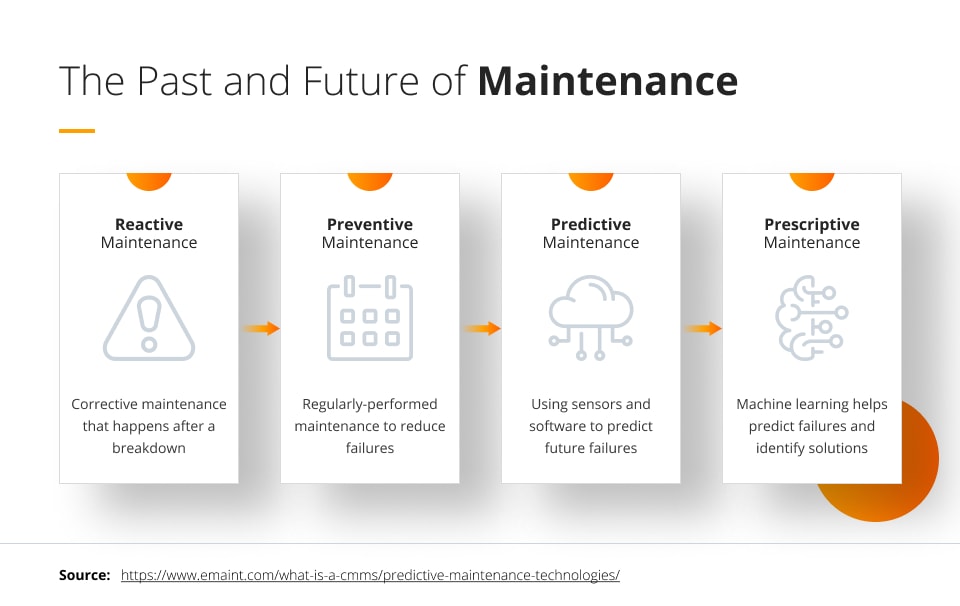
In today’s fast-paced world, organizations need to stay on top of maintenance issues before they become critical. Predictive maintenance (PM) is one such strategy that utilizes data, analytics, and machine learning to predict potential equipment failure before it occurs, preventing costly downtime and repairs. In this article, we explore how augmented reality (AR) and cloud computing are transforming the future of predictive maintenance.
AR technology provides an intuitive and engaging way of visualizing complex data and information, making it an ideal solution for predictive maintenance applications. Cloud computing, on the other hand, allows for remote access and monitoring of the sensor system, reducing maintenance costs and complexity. We will also look at some real-world examples of AR and cloud-based PM solutions across various industries.
Augmented reality and predictive maintenance
Augmented reality (AR) technology is transforming the maintenance industry with its intuitive and engaging way of visualizing complex data and information, making it an ideal solution for predictive maintenance applications. By integrating AR into maintenance workflows, organizations can improve maintenance efficiency and effectiveness, reduce downtime, and increase equipment uptime and cost savings.
With AR, maintenance personnel can easily access a clear, real-time view of machine health, allowing them to quickly identify and resolve potential issues before they become critical. Additionally, AR enables remote collaboration, allowing maintenance teams to collaborate and share knowledge across multiple locations.
One of the most significant benefits of AR in maintenance is the ability to provide immersive and interactive training experiences for maintenance staff. AR-based training can help reduce onboarding time and improve training effectiveness, leading to better overall performance and increased efficiency. AR can simulate real-world scenarios, allowing maintenance personnel to practice and learn in a safe and controlled environment.
Augmented reality technology can seamlessly integrate predictive maintenance analysis into an intuitive and interactive interface. This innovative approach magnifies the insights and findings derived from PM analysis, making it more understandable and useful for service employees. By creating an immersive environment, employees can feel at ease and in their element, leading to more effective maintenance practices and optimized equipment performance.
As with any technology, there are also challenges to implementing AR-based predictive maintenance solutions. One of the most significant challenges is data security and privacy. As more and more maintenance data is stored in the cloud, it becomes vulnerable to cyber-attacks and other security breaches. It’s essential for organizations to implement robust security measures and protocols to protect sensitive data. We will discuss more about predictive maintenance in the cloud later in the article.
Improving efficiency and training
One of the most promising applications of AR in maintenance is remote training and collaboration. By using AR-enabled devices, maintenance technicians can receive real-time guidance and support from remote experts. This is particularly valuable for organizations with dispersed teams or remote assets, as it allows for rapid troubleshooting and problem-solving. In addition, AR-based training can help to reduce the time and maintenance costs associated with traditional training methods, such as classroom instruction or on-the-job training.
Real-world examples of AR-based predictive maintenance solutions are already being developed and deployed across a range of industries. For example, in the aerospace industry, Airbus is using AR glasses to provide maintenance technicians with real-time guidance and instructions for complex maintenance tasks. In the oil and gas industry, Shell has developed an AR-based system that enables technicians to view real-time sensor data from equipment and identify potential issues before they lead to failure. And in the manufacturing industry, companies like Siemens and GE are using AR to improve maintenance efficiency and effectiveness by providing technicians with real-time information about equipment performance and maintenance history.
Predictive maintenance in the cloud
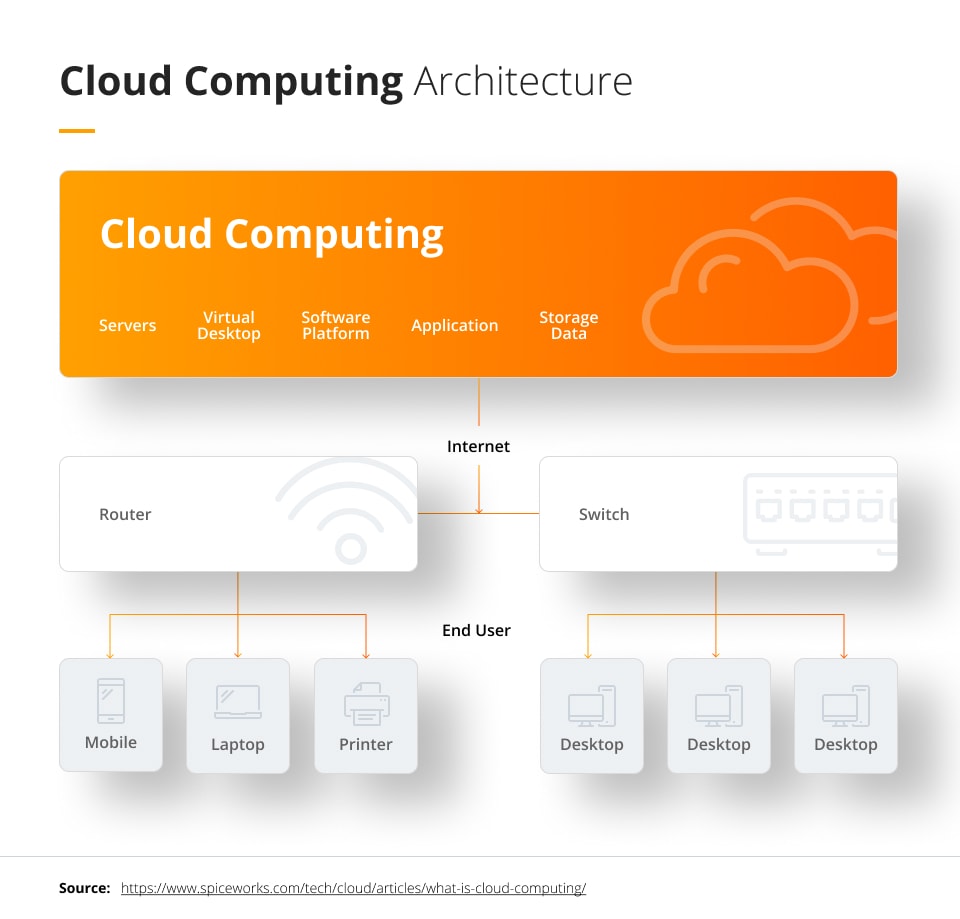
The predictive maintenance market is also being improved with cloud technology. The cloud includes servers that users can access through the internet, with all the software and databases running on the servers in data centers worldwide instead of on the user’s physical computer. It can do everything that physical servers typically do, including machine learning predictions, running tools to visualize historical component data, and service predictive maintenance issues. It also allows shared databases for users to access from different devices, reduces physical servers, and avoids the maintenance of software and servers.
Remote access
The biggest benefit of using cloud technology for predictive maintenance is the ability for maintenance teams to remotely access the sensor system for monitoring and testing purposes. This is convenient for the maintenance and monitoring team because it will enable on-demand access to the system without having to go to the sensors in person, allowing them to respond to sensors from anywhere. They can also give data access to outside experts for consultation when needed.
IoT setup
Cloud setup is often much simpler than installing on-premise servers. Instead of having to integrate multiple physical servers into the existing components, companies only need to connect their system to one server that can talk to the cloud. This gives more freedom when setting up the sensors, allowing them to focus solely on monitoring machinery and not setting up multiple servers.
Maintenance costs
Lastly, cloud systems decrease the cost of installing, operating, and updating software and license fees. Traditionally, companies will need to pay for and download software on their specialized infrastructure and pay for maintenance and support. They also need to pay for the physical computer and servers that the software will run on, as well as the pay for the maintenance of those servers.
This requires a lot of costs for the expertise required to set up and maintain everything, as well as the responsibility to continuously update the system for security and improvement purposes. On cloud systems, a lot of this work can be offloaded to another company or remotely maintained.
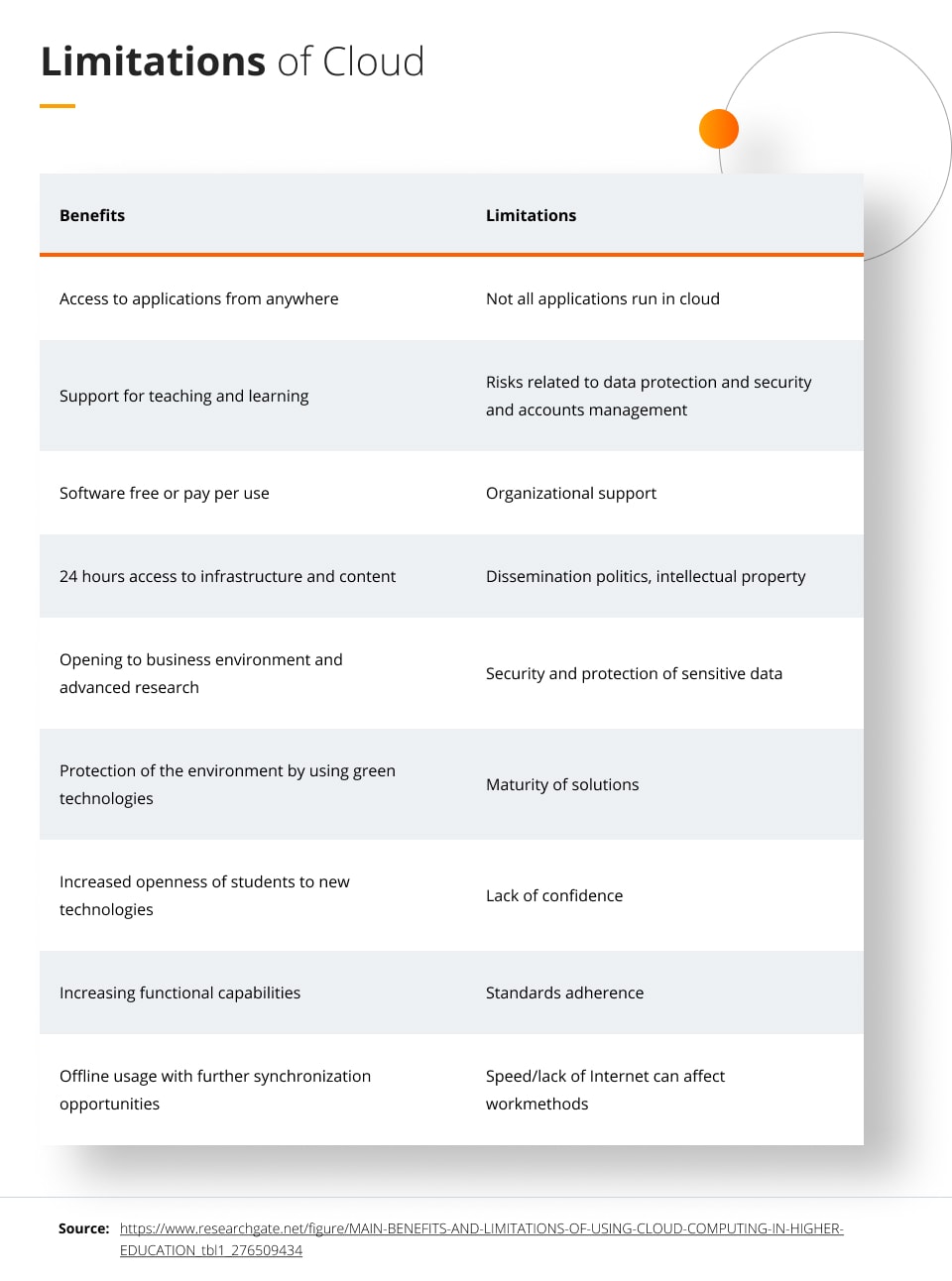
Limitations of cloud
Because the cloud is on the internet, it is more susceptible to hacking than an on-premise system. Without the cloud, someone would need physical access to the server and IoT system to access its data, limiting the potential for hacking or data loss. With the cloud, there are more opportunities for people to access the system through stealing login information, hacking into the software, and more. However, proper cybersecurity practices can limit the risk of this and keep the IoT system safe.
Robotics and predictive maintenance
Why use robotics?
Most data for predictive maintenance is collected through an internet of things, which is not very thorough. While the internet of things provides data that is more easily attainable, it does not cover areas that are not monitored by stationary sensors. This means that something could break or go wrong in a part of the equipment, and nobody would know because there are no sensors cataloging the machine failures. There can also be areas in equipment and on sites that are dangerous for maintenance personnel to enter and work in, making it impossible to conduct predictive maintenance procedures.
Autonomous robotic inspection technologies allow robots to complete these procedures in hard-to-reach areas without endangering maintenance employees. It also gives the maintenance workers time to complete other tasks that cannot be done by technology. Robots in predictive maintenance technologies can search enclosed spaces and detect signs of wear and tear, such as corrosion, before it becomes a debilitating problem and fixes it.
Some mobile robots have the ability to collect data and interpret it using artificial intelligence without any of the human errors that data interpreted by humans would be liable to. This means that employing robots in predictive maintenance not only expands the scope of maintenance but also results in more accurate information about necessary maintenance. Finally, robots are cheaper and easier to integrate than extra equipment sensors, making robotics the more practical option in predictive maintenance.
Other technology in predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance is predicting potential failures in systems and equipment reliability, and digital twins can play a big role in that. Digital twins are virtual replicas of real-world machinery, which can be observed for potential failure scenarios. They can also be used to test potential systematic failure patterns. These simulations can aid maintenance staff in decision-making about upkeep of the equipment.
Data from the simulations are continuously observed and analyzed for any signs of system failure, then further studied using tools such as Matlab/Simulink in order to categorize it, making decision-making easier. This makes it easier to recommend actionable insights based on the data.
Examples of robotics in predictive maintenance
AISTEC (All India Society for Electronics and Computer Technology) created a damage detection and analysis system that is a combination of virtual reality, unmanned aerial vehicles, and 3D models. The unmanned aerial vehicles catalog the frequency of infrastructure and take note of any changes over time, while virtual reality is used to plan the reconstruction of damaged infrastructure. This damage detection and analysis system can be used for reconstruction after natural disasters, serving a humanitarian purpose as well.
Conclusion
In conclusion, predictive maintenance powered by augmented reality and cloud computing is revolutionizing the maintenance industry. The integration of AR technology into maintenance workflows improves maintenance efficiency and effectiveness, reduces downtime, and increases equipment uptime and cost savings. AR-based training and collaboration can also help reduce the time and maintenance costs associated with traditional training methods.
Moreover, cloud technology offers remote access, IoT setup, and cost reduction for predictive maintenance, which are particularly useful for maintenance teams with remote assets. While there are security challenges, with the right security measures in place, AR and cloud-based predictive maintenance solutions can significantly enhance maintenance operations and reduce costs across various industries.