Business Process Mapping: The Key to Simplifying Complex Business Processes
If you want to create a new strategy, improve customer satisfaction or fix inefficient procedures, try process mapping. It is the first step to find out how things work and how you can improve the workflow. When appropriately visualised, the process can successfully change for the better. See how it's done.
What is business process mapping?
Business process mapping means creating a visual representation of workflow, including people and systems carrying specific tasks at various stages of the process.
In process mapping, we also include external factors that are meaningful in a particular process (e.g. legal regulations, procedures). But the most important thing is that by process mapping we want to achieve the defined business goal.
Business process mapping helps understand the causes, course and consequences of actions we take. Thanks to it, we can better understand people in the process, find gaps and identify problems and risks to achieve the company’s goal.
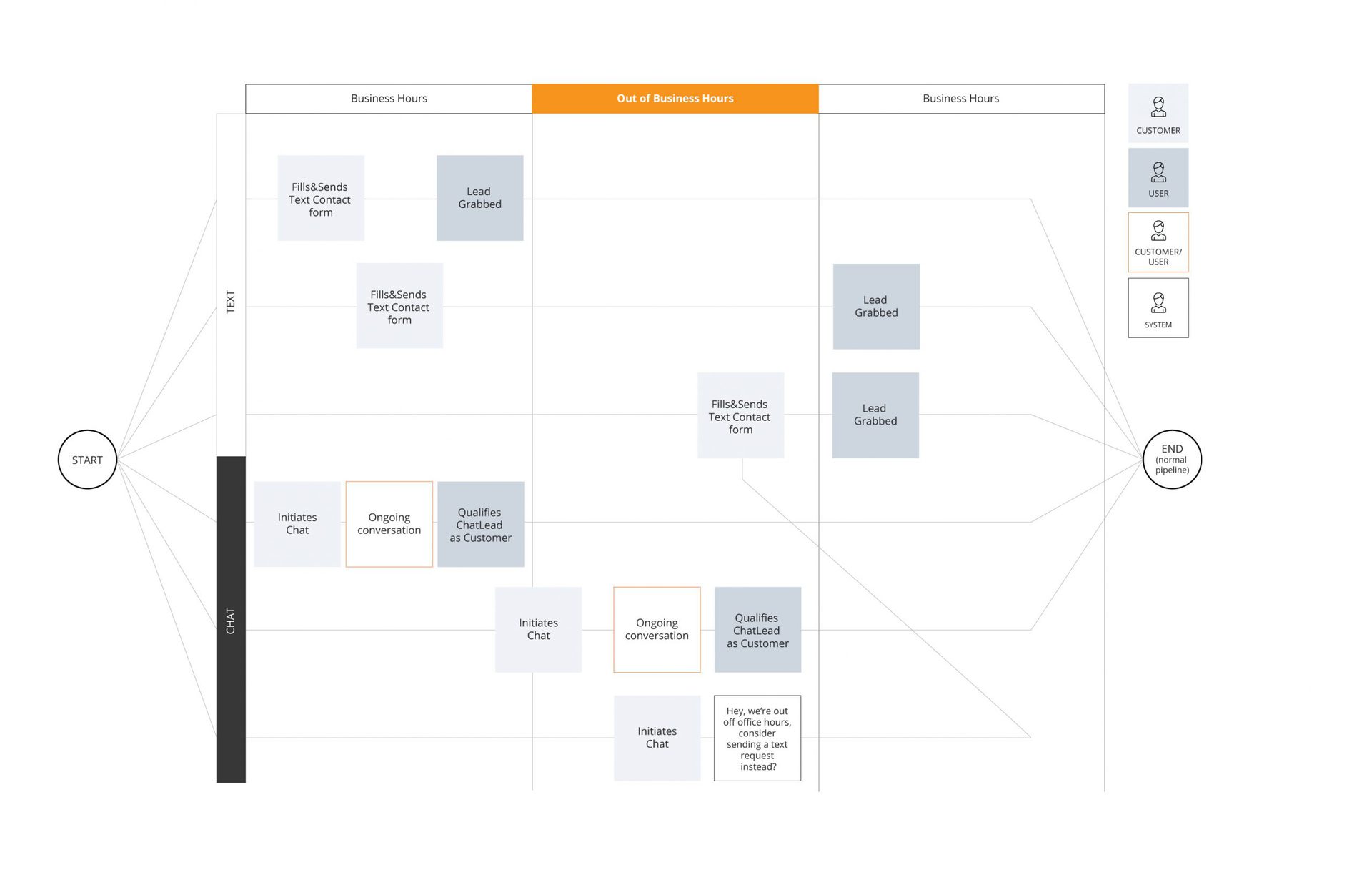
There are many different ways to build process documentation and draw detailed processes maps. We can use a flow process chart, diagrams, mind-maps and many other visual forms helpful in showing the workflow.
Here is an example of a process map:
How business process mapping helps companies?
Whenever the company is at the start of its business path or has been on the market for several years, at some point there is a chance for chaos, uncertainty, and process-related problems. While these moments are common for all, what changes is the level of companies awareness.
Businesses characterised by a high level of awareness know that process modelling is part of a more significant change where technology supports business. Thanks to modelling, they can effectively identify problems or ineffective processes inside the company or in customer care, and they can later improve them.
Businesses characterised by lower awareness of process mapping importance usually realise something is not working as it should. It may even happen that their clients realise that too!
Such organisations are often already in the process of digital transformation or they are introducing new departments, products or procedures. In their case, mapping is the best way to introduce order and modifications to improve their situation. Business process mapping is beneficial for all organisations.
Processes can be mapped in many different companies, such as:
start-ups,
businesses that are developing,
mature, large organisations,
businesses undergoing transformation.
Each of the companies mentioned above can map processes in case of organisational changes and new approaches (from organisational to human processes).
The principles of business process mapping
Key principles to consider when it comes to business process mapping include:
defining the purpose and scope of the process,
identifying stakeholders,
using consistent symbols,
focusing on the customer journey and work processes,
mapping sequential and parallel activities,
detailing each step,
seeking feedback and validation,
and maintaining simplicity throughout the entire process.
By adhering to these principles, organisations can create effective and valuable business process maps that serve as tools for understanding, analysing, and improving their operations.
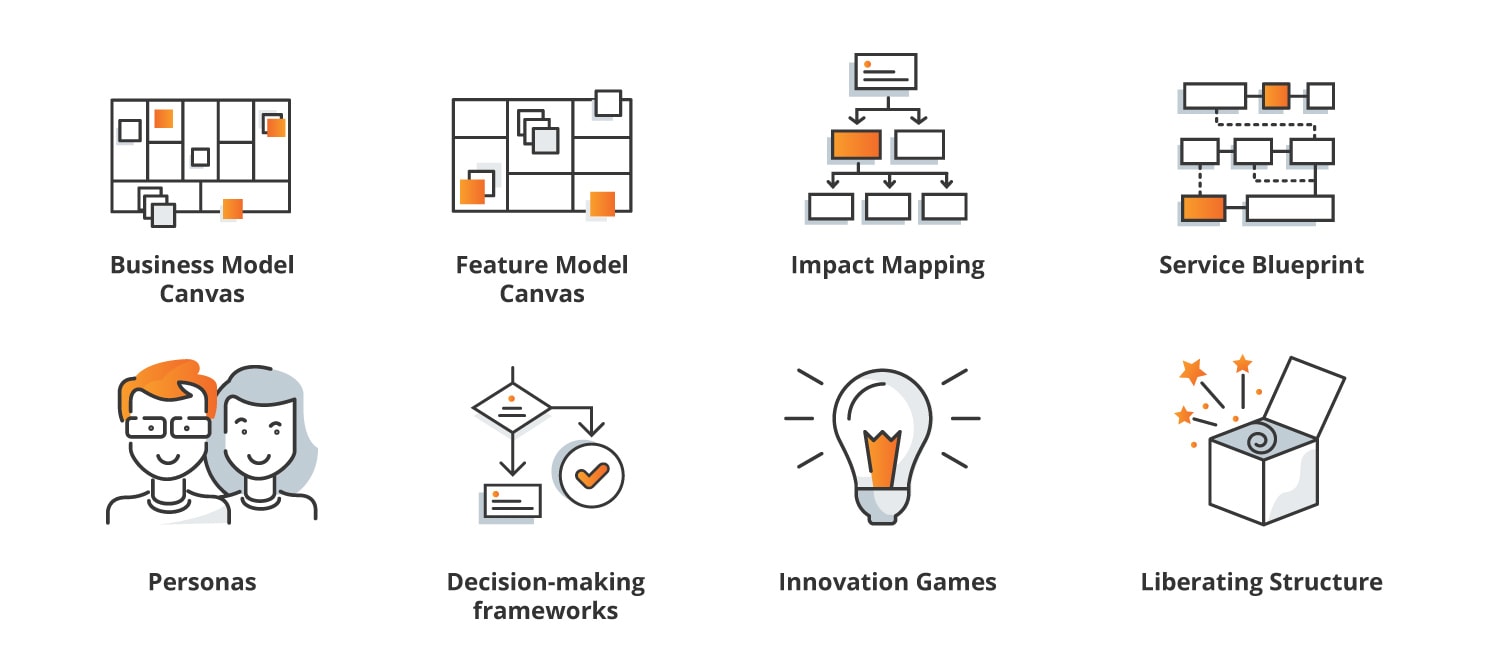
Types of business process maps
As business process maps can be created for project plans, documents, products, locations, strategies and others, and can be either very detailed or not, there are several types of business process maps, each serving a specific purpose.
Which one you choose depends on the goals of the mapping exercise, the complexity of the process, and the information required.
Here’s an overview of the main types of business process maps:
Flowcharts, one of the most common and versatile types of process maps. They use symbols to represent different elements of a process, such as tasks, decisions, and flows.
Data flow diagrams, which illustrate the flow of data within a system or process. They are particularly useful for understanding how data is input, processed, and output throughout the stages of a business process.
Swimlane diagrams divide the flowchart into lanes representing different departments, roles, or individuals involved in the process. This type of map clarifies responsibilities and interactions between different stakeholders.
Value stream maps focus on visualising the end-to-end process of delivering value to the customer. They highlight both value-added and non-value-added activities, helping organisations identify areas for improvement and waste reduction.
Narrative flowcharts combine text descriptions with flowchart symbols to provide a comprehensive understanding of the process. They include written explanations alongside visual representations of the process steps.
Benefits of business process mapping
Many companies wonder what do we get out of process mapping. There are many different business process mapping benefits, from financial, non-financial to those linked to work culture or sense of fulfilment.
The most significant ones include:
Gaining profits and reducing losses (both financial and non-financial);
Increasing efficiency and optimising process flow;
Identifying threats, gaps and challenges (risk management);
Gathering ideas for improvements of process performance and identifying possibilities of their implementation;
Acquiring knowledge, creating useful reports and documentation;
Raising awareness of processes, roles, responsibilities and duties among the team;
Reducing unnecessary complexity during development;
Increasing team performance and improving employee satisfaction.
Business process mapping: the process and the tips
Before we start mapping certain processes, we need to think about the details.
Those regarded as most essential ones include:
Identify the business processes for mapping
To start with, we need to define the beginning, full scope and end of the business process management initiative. It’s also time to list all its stakeholders and participants with the roles they will play at different stages.
Identification of the business goal of process mapping is crucial, as during this activity a team has to focus on the added value which will be delivered as an outcome.
Learn more:
Gather relevant information and people
Gathering relevant information and people means we need especially those who take part in the mapped process and those who impact it (e.g. management staff, specialists responsible for the systems or machines involved in the process). We will achieve the best results when all interested parties cooperate and share information.
All the people involved need to be focused on the task and willing to use their experiences, information and abilities. It’s essential to get involved without restricting or closing oneself.
Additional topics that may interest you:
Requirements Engineering: choose the workshop that best suits your needs
How can the discovery stage be powered by design thinking workshops?
Select the right process mapping tools and software
No matter what kind of situation we are currently in, we need to draw the whole process.
There are many valuable tools on the market like Draw.io or Miro. Primary types of diagrams for process mapping are BPMN (for creating process models in the form of flowcharts / diagrams) or UML (notation that allows you to present IT systems graphically, in the form of diagrams).
Depending on the chosen process, business goal, problem or a project an appropriate type of tool and diagram is selected.
Discovery workshops and creating the map
One of the most important parts of process mapping is Discovery workshops. By working with people involved, we do a step-by-step analysis of the whole process and its environment, ask and answer questions, contest different rules and procedures.
At Future Processing we believe that workshops are the most optimal way of process mapping, but there are also others. Together with our clients we plan steps we are going to take to improve processes within their company.
It is essential to sum up what’s been worked out and to draw conclusions from the workshops’ findings. Our report will guide the process according to what we agreed on during process mapping.
Analyse and identify improvements
A key to successful business process mapping is to regularly review the process map with stakeholders to ensure accuracy and completeness. It’s crucial to validate the map against the real-world process and make adjustments as needed.
Implement changes and monitor results
From theory to practice, it’s time to plan the details of every step of the process.
To do it, we need to know who and how will do specific tasks, and we need to discuss their effect. Then comes the most challenging part, which is the implementation and/or development of changes.
Optimising business performance with Future Processing
Even if some may think the processes should be mapped only once, the reality is entirely different. Things change dynamically, our environment and the internal view of the company continuously transform.
This is why many processes require further mappings and changes to adapt work to the reality. For this reason process mapping should become a constant common practice in companies wanting to keep up and develop.
Keen to kick start your business process modeling and look into your business process map? Do get in touch with our team – at Future Processing we have extensive experience in business process management and are dedicated to the continuous improvement.
We will be happy to share our business processes knowledge with you!