Deployment models and considerations of cloud migration
This article reviews the four deployment models, which allow companies to safely transfer their applications, databases, and other components to the cloud.
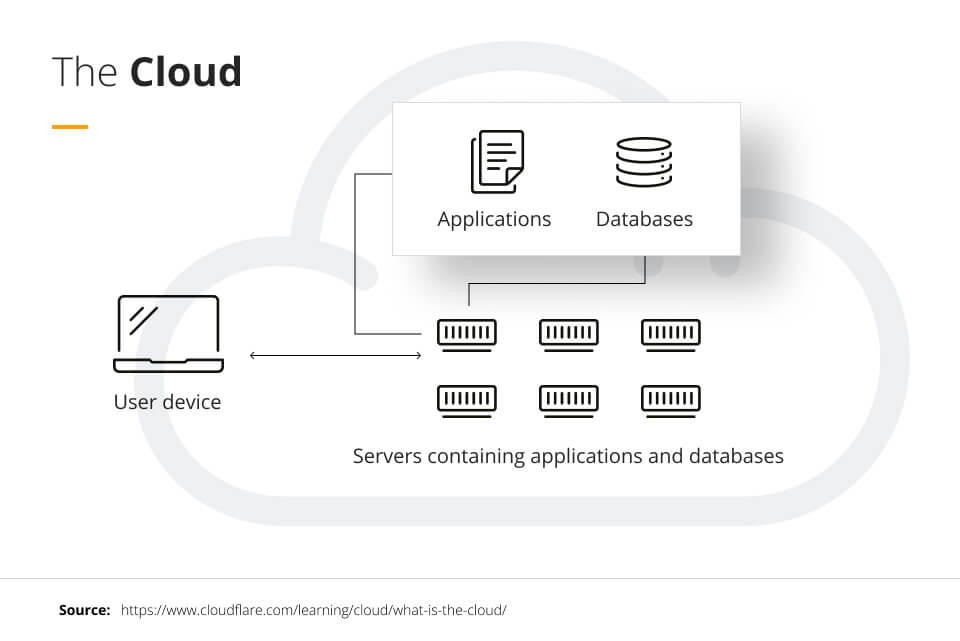
Migrating to the cloud has many advantages, such as scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. Having all applications on the cloud also makes disaster recovery easy, as there are typically backups on the cloud if any applications or components are lost.
This article reviews the four deployment models (public cloud deployment, private cloud deployment, community cloud deployment, and hybrid cloud deployment), which allow companies to safely transfer their applications, databases, and other components to the cloud. This includes examining several considerations companies should explore before deploying to the cloud. Finally, this article describes the impact of cloud deployment on business and explains the steps of cloud migration.
Cloud deployment models
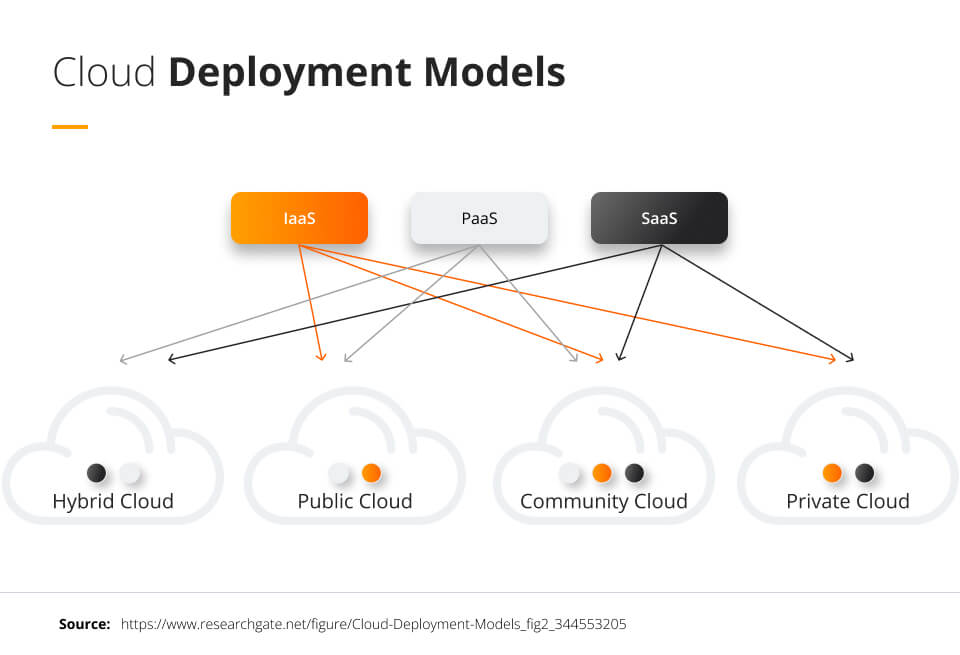
There are four main types of cloud deployment models, each with its own advantages and disadvantages when considering resources, computing requirements, networking, storage needs, and business goals.
Public Cloud Deployment Model
A public cloud deployment model is available for public use and is managed by a third party that allows multiple businesses and users to use its servers.
The cloud service provider is responsible for resource management and upkeep, as well as hardware maintenance, giving users on-demand resources. This is the most popular deployment model, with popular cloud services being AWS Elastic Compute Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
Public cloud deployment models are convenient due to the service providers managing resources, reliable due to service providers having large server networks, and they usually offer highly scalable plans. This makes it cost-effective and allows businesses to only use the resources they need without downtime.
The biggest issue with this model is potential security issues around data and privacy due to customers not directly managing data. Also, many service plans are simple to appeal to many but may not be as customized as some businesses want. Lastly, there are chances for service outages on the entire network.
Private Cloud Deployment Model
A private cloud, also called a corporate or internal cloud, is only used by one business. It can be hosted on-premise by the company or hosted by a third party, and only a single company can access the cloud hardware and software. This is the second most popular model, and HP and Dell offer these models.
Opposite to the public cloud model, the private cloud’s advantage includes high security and privacy because only the company can access the data.
Additionally, models can be customized and tailored to that company’s needs since only they are using it. It is also relatively reliable and can be scaled by adding more hardware.
Private cloud deployment does come with a high initial cost to obtain the hardware, licenses, and software to establish it, as well as training and staff to maintain it. However, if the initial investment is made and everything is properly set up, it could save money in the long run.
Community Cloud Deployment Model
A community cloud is owned by one organization and shared with multiple businesses with similar characteristics, usually with similar computing requirements. This allows the community using it to collaborate on projects and share the cost of maintaining the cloud.
This model allows for cost savings by splitting the cost among partners, high security due to data access being limited to established partners, and allows collaboration between users and organizations.
However, it is often hard to find other organizations with similar characteristics and computing needs, making it an uncommon model.
Like the private cloud, it also has a high initial cost with the potential for long-term savings. Additionally, there is the chance for resources to run out as multiple resources use the same bandwidth, computing, and storage capacity.
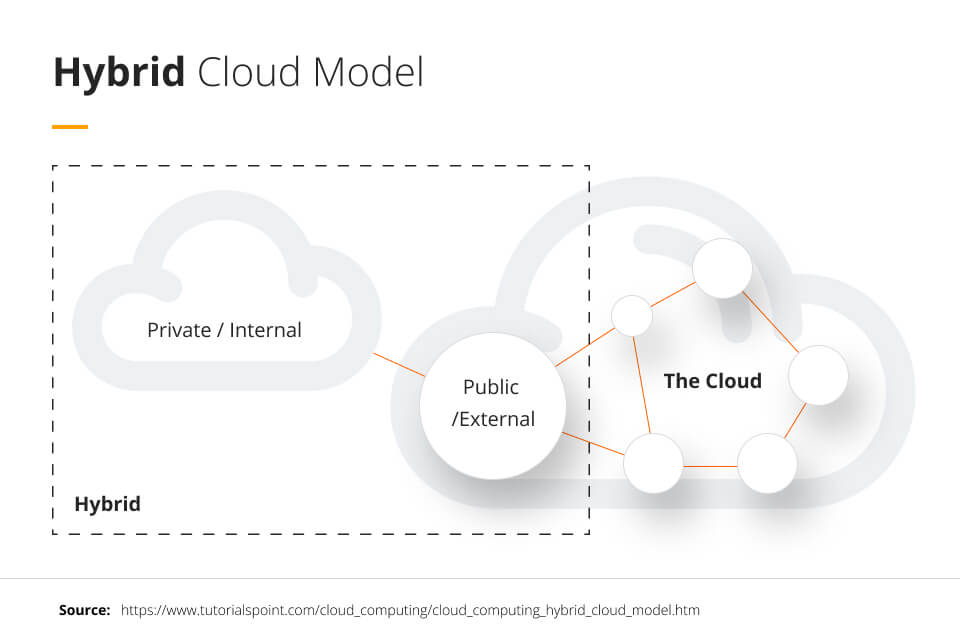
Hybrid Cloud Model
The hybrid cloud model takes elements of each of the above cloud models and creates a hybrid model that pulls from the advantages of each. This allows for high levels of customization when it comes to data security, resource usage, and flexibility. However, implementation can be complex and is best handled by service providers with experience in deployment.
Considerations when migrating to cloud
When considering migrating databases and custom applications to the cloud, it is important to evaluate the suitability of the application for the cloud. Not all applications are cloud-ready, and it is essential to assess the performance, security, and compatibility of the application.
This includes evaluating the application’s architecture, dependencies, and resource requirements. This assessment will help minimize disruptions during the migration and ensure that the application runs smoothly after the migration.
Selecting the right cloud provider
Selecting the right cloud provider is another crucial consideration when migrating to the cloud. It is essential to choose a provider that offers high levels of security, compliance, and scalability to meet your specific needs. This includes evaluating the provider’s security protocols, data center locations, and certifications.
Additionally, it is vital to ensure that the provider has adequate backup and recovery mechanisms in place to protect your data in case of unexpected downtime.
Performance
Performance is another vital factor to consider when migrating to the cloud. It is crucial to evaluate the application’s workload requirements and select the appropriate cloud infrastructure that can handle the workload.
Cloud providers offer various performance tiers, and it is imperative to select the one that meets the specific needs of the application. This includes evaluating the provider’s network bandwidth, storage options, and compute resources.
Cost
Cost is another significant factor to consider when migrating to the cloud. While the cloud can offer significant cost savings compared to traditional on-premises infrastructure, it is essential to evaluate the TCO of the cloud solution. This includes the cost of migrating, operating, and maintaining the application in the cloud.
It is also vital to consider the pricing structure of the cloud provider, including any additional costs for data storage, network traffic, and other services.
Planning
Planning is also critical to a successful migration. It is crucial to create a detailed migration plan that includes timelines, milestones, and testing protocols to ensure a smooth transition. The plan should also include contingency measures in case of unexpected issues during the migration. By planning carefully, businesses can minimize disruptions and ensure a successful migration.
Regulation and legislation
Another major concern when undergoing cloud migration is regulation and legislation. It is important to ensure that cloud migration operations are compliant with all applicable rules in a rapidly evolving legal space. This is especially the case when data is crossing international lines.
It is also important to carefully consider the contract between the company migrating to cloud and the cloud provider. Some important considerations include stipulations in case of disaster, data collection and privacy policies, intellectual property protection, and service interruption.
The impact on end-users
The impact on end-users is another significant consideration when migrating to the cloud. The application’s user interface may change during the migration, and it is crucial to communicate the changes to the end users to minimize confusion and disruption. This includes providing training to end-users on the new system and ensuring that the system is user-friendly and easy to navigate.
The migration of ‘data analytics solutions’
The migration of ‘data analytics solutions‘ is a unique and specialized process within this field. It is important to note that various types of data formats are available, including both closed and open formats. When selecting a service provider, the choice of data format can significantly impact future operations.
For example, AWS Redshift and Snowflake employ closed data formats, while Azure Synapse (in preview version) and Databricks support open data formats.
During the MS Build conference, Microsoft openly expressed its commitment to developing and supporting available data formats, as evidenced by its release of Microsoft Data Fabric, a transformative innovation in this domain. Additionally, migrating the data analytics platform to the cloud requires careful consideration and implementation.
It often entails rebuilding the entire data infrastructure and business logic using cloud-native services to ensure a successful transition.
This process involves modernizing the whole data landscape within the organization, taking advantage of the capabilities offered by cloud technologies. By embracing cloud-native services, companies can optimize their data analytics platform and unlock new possibilities for improved efficiency and innovation.
Data backup and recovery strategy
Having a robust data backup and recovery strategy in place before migrating to the cloud is vital. This ensures that data is not lost during the migration process and can be recovered in case of unexpected downtime or data loss.
However, being able to ensure data restoration is not the only consideration. It is also important to ensure that information remains available in the event of disasters. It is essential to evaluate the provider’s backup and recovery mechanisms and ensure that they meet your specific needs.
Business Impact of Moving to the Cloud
Migrating to the cloud can have a significant impact on a business, both in terms of its operations and bottom line. By leveraging the flexibility and scalability of cloud computing, businesses can improve their agility and responsiveness to changing market conditions. This can enable businesses to rapidly develop and deploy new products and services, improving their competitive position in the market.
Cloud migration can have a positive impact on a business’s financials. By reducing the need for physical infrastructure, businesses can significantly decrease their IT infrastructure costs.
Furthermore, it is worth mentioning that cloud providers often offer pay-as-you-go pricing models. However, it’s important to note that for customers, partnering with cloud providers can be even more beneficial.
Partnerships often come with exclusive discounts and advantages, which can further contribute to cost savings. This approach allows businesses to pay only for the resources they use while enjoying the benefits of discounted rates through their partnerships. As a result, significant cost savings can be achieved over time, enabling businesses to allocate freed-up resources to other essential areas of operation.
However, it is essential to acknowledge that in some cases, legislation can pose challenges and be an issue when it comes to cloud migration. Compliance with industry-specific regulations and data protection laws must be carefully considered and addressed.
Failure to adhere to these legal requirements can lead to severe consequences, including financial penalties and reputational damage. Additionally, cloud migration can also have negative impacts if not planned and executed properly.
Disruptions to employee workflows and productivity, as well as potential vendor lock-in and compliance issues, can result in unexpected costs and delays. It is crucial for businesses to carefully evaluate the potential impacts of cloud migration, including the legal landscape, and plan accordingly to minimize risks and ensure a successful transition.
By proactively addressing legislation and compliance concerns, businesses can navigate potential obstacles and ensure a smooth and legally compliant cloud migration process.
Ultimately, the impact of cloud migration on a business depends on a variety of factors, including the business’s size, industry, and specific needs. By carefully evaluating the benefits and drawbacks of cloud migration, businesses can make an informed decision that aligns with their goals and objectives.
With the right planning and execution, cloud migration can be a powerful tool for businesses looking to improve their agility, scalability, and bottom line.
In conclusion, migrating to the cloud can offer significant benefits to businesses, but it is important to carefully consider several critical factors to ensure a successful migration.
These include evaluating the application’s suitability, selecting the right cloud provider, ensuring adequate performance and security, evaluating the TCO, planning the migration process carefully, considering the impact on end-users, and having a robust backup and recovery strategy in place.
By carefully considering these factors, businesses can successfully migrate to the cloud and enjoy its numerous benefits.
How to migrate to the Cloud?
Ways to Migrate to the Cloud
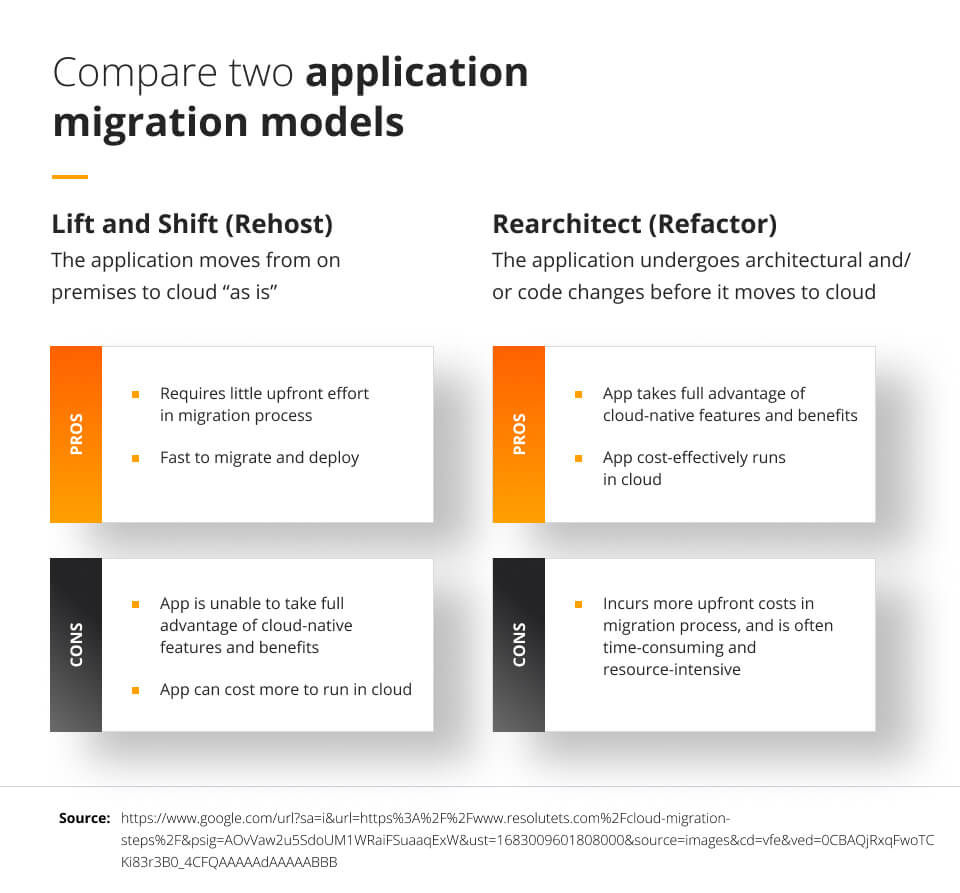
While there are numerous ways to migrate to the cloud, 3 of the most significant ways to migrate to the cloud include: the lift-and-shift method, using software as services, and building solutions native to the cloud. Each of these comes with its own advantages and disadvantages.
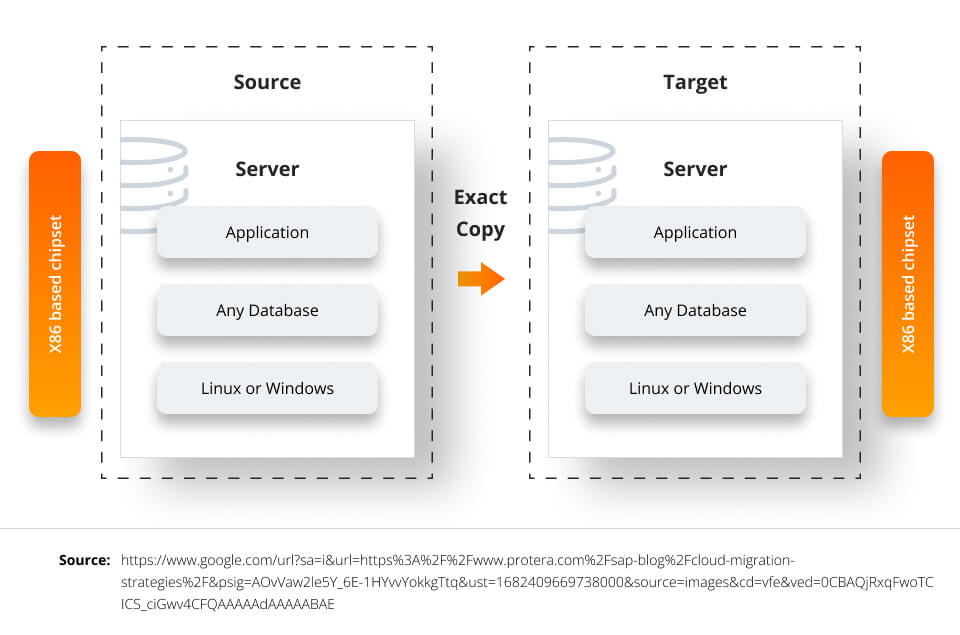
The lift-and-shift method involves moving an application to IaaS (infrastructure as a service) in the cloud as is, without any changes to it. While this is an immediate solution to migrating to the cloud, all existing bugs in the applications would remain there until someone specifically fixes it.
Applications moved using the lift-and-shift method also have less availability built in, as they were not created to adapt to different digital environments.
Software as a service is a popular way to migrate to the cloud, as it is accessible, cheap, and native to the cloud. Some examples of software as a service include Adobe, Microsoft 365, and Google Workspace. However, since this software is popular, companies that rely on them can have trouble differentiating their businesses from others in the industry.
Finally, companies can use platforms as a service to create applications that are original to the cloud. This allows them to clean out applications that can only be used on certain devices and build new applications that take full advantage of all the services the cloud has to offer.
For example, they would be able to store and access large amounts of diverse data for analytics. However, when companies rely too much on platforms as a service, they can vendor-lock themselves to a cloud provider. This means that if the cost of the provider increases suddenly, the company would be forced to pay.
Steps of Cloud Migration
There are a variety of steps and considerations that businesses should undertake in order to properly execute cloud migration:
- The first step is to establish the purpose of migrating to the cloud in a business context and to conduct a proper assessment of the current state
- Based on this information, the next steps are to choose a cloud environment and determine an ideal deployment model, whether it be software as a service or platform as a service.
- Next, ascertain the costs of different types migration, and what the company needs.
- While prioritizing migration components, the next steps in the cloud migration process are to fix baselines for performance and construct a plan for data migration.
- Then, the company should migrate the applications according to the plan.
- The company should then revise all the applications and components that were moved to make sure that nothing is missing and everything is in the proper condition.
- Next, the company should shift its domain and associated IP addresses to the applications on the cloud.
- The next step is to test all the components in the cloud to make sure they work properly.
- After this, the company needs to perform security assessments in order to make sure that there are no vulnerabilities.
- Finally, the company should pick a cloud partner and architecture that caters to all its needs while staying within its budget.
Conclusion
Cloud deployment is a good way for companies to back up their applications and databases while making them more accessible. As each cloud deployment model offers different advantages, it is important for companies to choose one that best fits their own budgets and necessities.
Cloud deployment and migration can improve an application’s scalability and accessibility, oftentimes increasing the worth of the application. While there are many things to take into consideration before transferring, companies have much to gain from cloud deployment.