How to implement cloud computing?
Uncover the basics of cloud computing, including service models and providers, as well as how to implement cloud and common use cases.
Introduction
Cloud implementation is a hot topic, with organizations and companies looking to find ways to implement it into their technology. Already, around 60% of corporate data is stored in the cloud, doubling since 2015. The global cloud computing market is estimated to be worth over $500 billion, with its value growing by the year.
This is unsurprising, considering all the benefits that cloud computing provides and the variety of options consumers can choose. In this article, we will cover the basics of cloud computing, including service models and providers, as well as how to implement cloud and common use cases.
Cloud computing basics
Cloud computing has become an essential technology for modern businesses, providing a cost-effective and flexible way to access computing resources. Simply put, cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services, including servers, storage, databases, and software applications, over the internet. This allows businesses to access these resources without the need for expensive hardware and infrastructure investments.
One of the key benefits of cloud computing is scalability. With cloud computing, businesses can easily scale their computing resources up or down as needed without the need for costly hardware upgrades. This can save businesses significant time and money, as they can quickly adapt to changing market conditions and customer demands. Additionally, cloud computing offers economies of scale, as cloud providers can take advantage of their large customer base to offer lower prices and better service.
Another advantage of cloud computing is accessibility. With cloud computing, users can access their applications and data from anywhere, as long as they have an internet connection. This allows remote work and collaboration, as well as increased productivity and flexibility. Additionally, cloud computing providers invest heavily in advanced security features and certifications to ensure the protection of their customers’ data, offering a higher level of security than traditional on-premises solutions.
Next important benefit of cloud computing is its ability to enable innovation. Cloud computing provides access to a wide range of cutting-edge technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things. These technologies can help businesses to gain new insights into their operations and customers, leading to better decision-making and competitive advantage.
Cloud computing can also help businesses to improve their disaster recovery and business continuity capabilities. With cloud computing, businesses can easily replicate their data and applications across multiple geographic regions, ensuring that they can quickly recover from disasters such as natural disasters or cyber-attacks. Additionally, cloud computing providers often offer robust backup and recovery services, further improving the reliability and availability of critical business data.
In conclusion, cloud computing has become an essential technology for businesses of all sizes. By providing cost-effective and flexible access to computing resources, cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate and compete in today’s fast-paced market. With its scalability, accessibility, and advanced security features, cloud computing is poised to continue to shape the future of business for years to come.
Cloud Computing Service Models
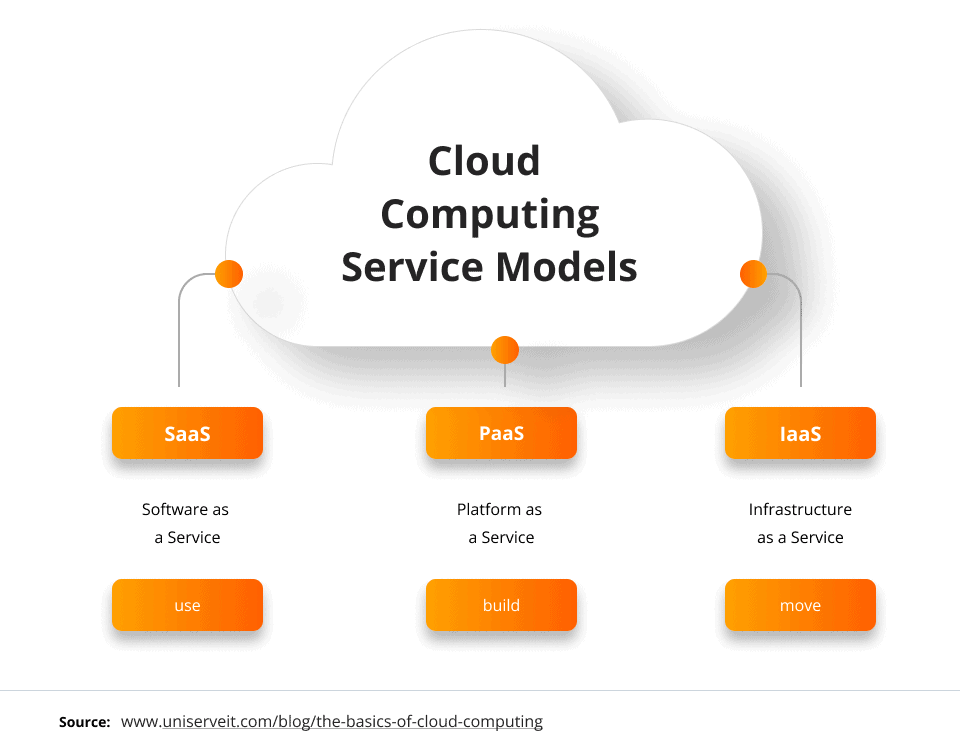
Cloud computing has become an essential technology for businesses looking to reduce costs and improve their operational efficiency. There are three primary service models in cloud computing: Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Platform as a Service (PaaS).
SaaS is the most common option for private users, where software applications are hosted by the vendor or service provider and made available to users over the internet. This service model is recommended for small companies that require collaboration between teams and need applications that are accessible via web and mobile.
IaaS, on the other hand, allows users to rent their entire IT infrastructure from a service provider and pay corresponding to their use. This service model is recommended for businesses that require increased security and need control over the infrastructure.
PaaS provides a facility for users to publish and customize software applications in a hosted environment. This service allows developers to create applications faster without the need to configure the infrastructure. PaaS is a good option for businesses that are planning to create a customized app and have multiple developers working on the same project.
In conclusion, selecting the right cloud computing service model is essential for businesses to achieve their goals and optimize their operations. By considering factors such as collaboration, infrastructure control, and application customization, businesses can select the most suitable service model that aligns with their specific needs and objectives.
Implementing cloud computing
Steps to Implement Cloud Computing
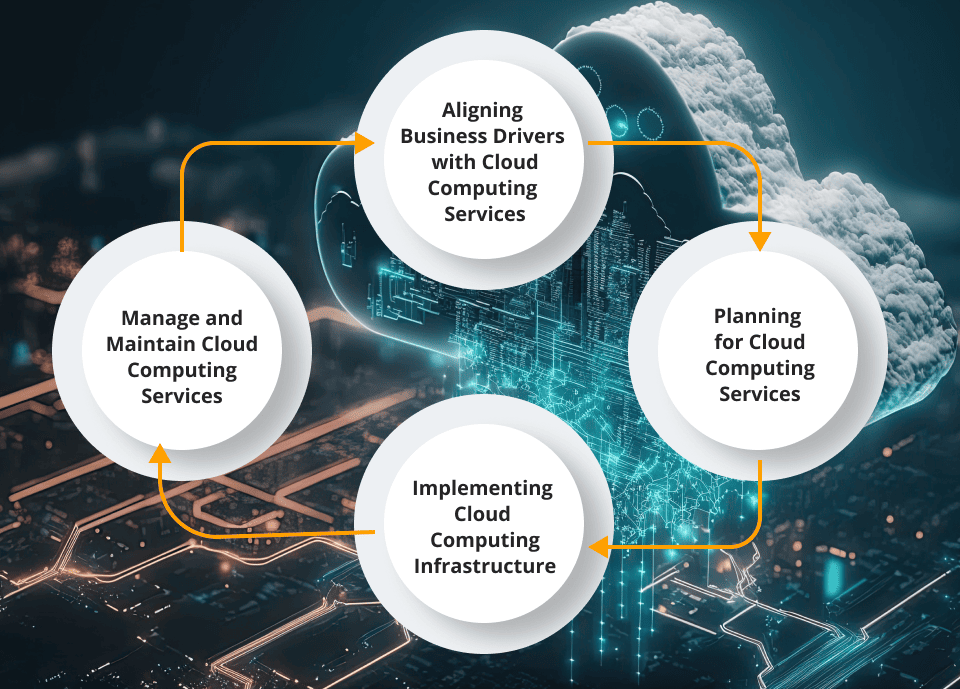
The first step to implementing cloud computing services is determining the objective of implementing it; that is, the company must first figure out why they want to use cloud computing services in the first place. This includes investigating the weaknesses of the service they currently use, and setting a clear-cut goal for how data will be stored after implementing cloud computing.
The next step is planning out a beginning, middle, and final state of data storage for the company in terms of implementing cloud computing. After conducting a current state analysis on the IT service that is used at the time, it is then necessary to plan what the state of data storage and recovery will be during the implementation phase, and after. It is also important to decide which cloud model would work best based on the weaknesses of the current service provider outlined in Step 1. The final component of Step 2 is to plan how to sustain the new cloud computing model for long-term use.
The third step of cloud computing implementation is actually implementing the new service provider. Ways of carrying out this step vary depending on if the company selects a public, private, or hybrid cloud model.
The fourth step of implementing a new cloud service provider is initiating a maintenance model for long-term use. This includes the business side (building value metrics and making sure it holds enough data) and the IT side (spotting and fixing any system bugs or failures, and ensuring that security and feature updates are up to date). This final step is an ongoing process, as bugs must be repaired as they pop up, and requirements for the cloud model could often change. Part of the last step is to continue to enhance the cloud model in order to cater to changing requirements. The managed service provider also has to continually focus on ongoing security enhancements, resilience improvements, and capacity planning to ensure the highest level of protection and operational efficiency for their clients’ systems.
In addition to these steps related to updating the technology and processes in place, companies need to prepare the people, or human resources, to properly leverage cloud technology. Companies may need to hire new employees with the skills to work with cloud technology, train old employees to use new technology, and prepare for employees who may resist this change. Many companies have been using the same process for a while, and because humans naturally feel uncomfortable with change they need to have plans in place for employees who will resist implementing cloud technology because they have been using the same old process for years.
Cloud Computing Providers
A cloud computing provider is a company that offers computing resources that can be accessed over a network, such as computing, cloud-based storage, platform, and application services that are adaptable to the needs of businesses. These companies specialize in managing and optimizing data retrieval, storage, and distribution on the cloud.
Some of the top public cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, Alibaba Cloud, Oracle Cloud SaaS, and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). Although all of these providers are part of the top 10 public cloud service providers, they each have their own advantages and disadvantages.
For example, AWS is the largest cloud service provider in the world, with its user-friendly, flexible, secure, and cost-effective nature. However, this provider sets limits to the resources available to users, and it requires some unforeseen hardware changes. Furthermore, although Google Cloud Platform allows users to use AI and analytics to create and test applications, it can be expensive, and customization is limited. Alibaba Cloud, the primary cloud vendor in Asia Pacific, offers machine learning and big data analytical capabilities, as well as network virtualization; however it is not very popular outside of Asia, and there are not many integrated tools such as security and administrative tools. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure offers low costs and unparalleled accessibility, but it does not help streamline low-end activities.
Some top private cloud providers include Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE), VMware, Dell’s APEX, and Microsoft Azure. HPE, VMWare, and Dell offer hybrid solutions that integrate well with their technologies and often cooperate with AWS or Azure to use their on-premise deployment. Although these are part of the top 10 private cloud computing providers, each has its own benefits and disadvantages.
For example, although HPE is very scalable, with good customer support and a smooth initial setup, it can be too expensive for some users. VMware engages in life cycle management and is very helpful when creating new applications, with a strong disaster recovery system. However, its documentation is not as efficient as other private cloud providers. Dell APEX offers the ability to forecast, has fewer infrastructural vulnerabilities compared to other providers, and has strong dashboards. However, this provider is catered mostly towards users of Dell products, so it can be difficult for users of other brands to use APEX. Finally, even though Microsoft Azure is the second-to-top cloud provider in the world, with its BOT and Computer Vision services and machine learning frameworks, it can also be more difficult for smaller businesses to afford. However, It is worth noting that a lot of cloud providers are expensive, and may be too costly for small businesses to implement.
Cloud computing use cases
There are various use cases for cloud computing, as well as service models and service providers that are optimized for each use case. The types of use cases increase as technology develops, but there are several popular ones that are widely used.
Testing and Development
The cloud can be used as a software development environment, with teams using it to develop and test a production environment via provisioning physical or virtual machines. Using the cloud instead of in-house development saves the time it would take to install and configure the development platform, which can thus be used in the development process.
Cloud services often include features that aid this process, like DevOps facilitation, microservice integration, and deployment pipelines. Some services, like microservices, serverless deployment, and containerization, are cloud-native features and cannot be implemented on in-house deployment. Popular cloud service providers include Microsoft, which has a special cheaper subscription for development only, and AWS, which has a variety of options with different optimizations. Both of these providers also offer some financial support for their development cloud services.
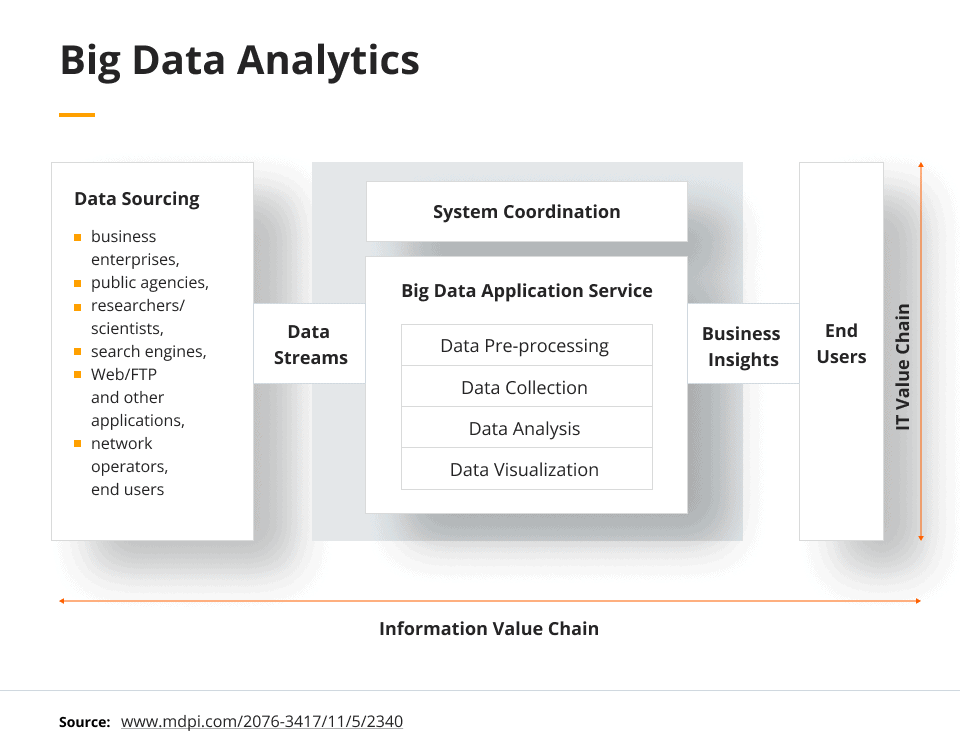
Big Data Analytics
Companies will often have large amounts of data from everyday activities, and running big data analytics will allow them to collect insights to improve their business processes. Users create data from transactions, interactions, and data they willingly give to companies. One example of this is analyzing buying patterns and customer preferences to develop a marketing campaign.
Handling such large amounts of data is a challenging process, but there are many cloud platforms that offer big data services. These services include database management systems, identity management systems, and machine learning features. Users can also search and edit data, as well as process it, to gain insights.
Cloud Storage
One of the most popular uses is cloud storage, where files and other data are saved directly to the cloud. This allows any device with an internet connection to access the data from any location. Rather than having to physically build and maintain a data center, they can pay for cloud storage and rely on service providers to maintain it for them.
Cloud storage offers the benefit of “pay-as-you-go” plans, or only playing for the resources used rather than for all of the data centers. Additionally, they usually build data centers across the world, allowing for higher availability and recovery in the case of a shutdown or natural disaster. Companies should look into data privacy laws before using the cloud, as some data may be required or recommended to be kept on-premise.
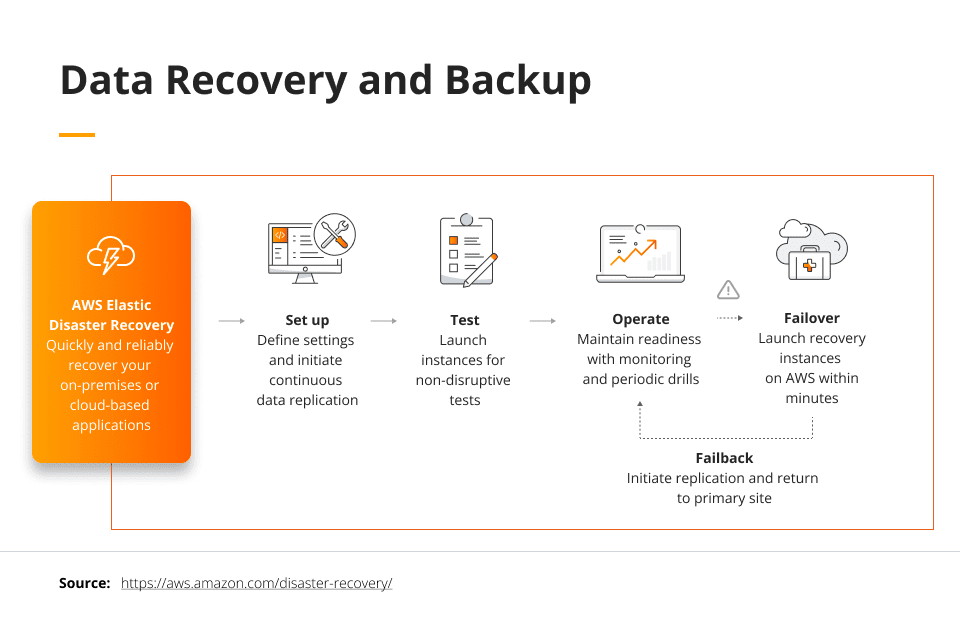
Data Recovery and Backup
Another big use case for cloud computing is disaster recovery and data backup. Organizations can replicate their production site, configuration settings, and data in their cloud, saving the time and resources needed to create a designated disaster recovery site. Similarly, organizations can back up their data to a cloud data center without having to worry about security or capacity issues.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has become an essential technology for businesses and organizations of all sizes and industries. Its cost-effectiveness, scalability, and security features have revolutionized how businesses operate in today’s high-tech and fast-paced market. By implementing cloud computing, organizations can use on-demand computing resources for deployment, storage, analytics, and many more use cases. However, it is important to determine objectives, business needs, and long-term plans when implementing the cloud and not rush into it. By creating a proper cloud strategy plan, organizations can ensure a successful cloud implementation and harness the full power of the cloud and drive success.