Public Cloud vs Private Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud: what are the differences?
In recent years, there has been a strong trend for companies to opt for a cloud computing-based strategy for their organisation. This cloud migration strategy has been gaining traction, as it allows businesses to store their data safely in the cloud, as opposed to on their physical drives.
By using well-established cloud services, companies can utilise cloud computing resources and expect greater security procedures, an increased ability to scale up their operations and potentially huge cost savings.
What are Private Clouds, Public Clouds and Hybrid Clouds?
There are three main types of cloud networks:
- Private – This is a private cloud infrastructure that is created exclusively for a business. It is usually set up on-premises but can be expensive to build and maintain.
- Public – This is a public cloud infrastructure that is owned and maintained by specialist cloud service providers and is available to individuals and businesses alike.
- Hybrid – This is a hybrid cloud solution that combines public and private clouds, selecting aspects of both.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is a dedicated infrastructure that is exclusively used by a single organisation. In the private cloud, all data remains firmly in the control of the company, which doesn’t share any of its resources with anyone from outside the organisation.
Sometimes referred to as a ‘data centre’, private clouds are hosted either on-premises or in a third-party centre and are managed by the organisation’s IT staff. All resources are hosted and delivered on a private and secure network, making it very safe.
Private infrastructure is highly customisable to the specific needs of the company. This allows organisations to have a greater degree of control over their infrastructure and work with sensitive information without worrying about their security and helping to improve performance and efficiency.
Public Cloud
A public cloud is a shared infrastructure that is accessible to anyone on the internet. Public cloud providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform, offer a range of services, including computing power, storage and applications.
The public cloud infrastructure is delivered via the internet, making it the most widely used and popular model of cloud computing today. They are extremely varied and offer many different choices for companies who are making a digital transformation to help them address the modern needs of their business.
Some public cloud services are free, but they tend to be limited in their scope and functions. Typically, companies will tend to opt for a subscription-based model whose price will vary according to their storage needs and the types of tools they require access to.
The vendor offering a public cloud infrastructure is responsible for the maintenance, security and development of the platform, allowing companies to focus on their business operations. While it is called public cloud, the customers can isolate their environment from the outside world making it secure for internal usage only.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud is a combination of public and private clouds that are interconnected. Organisations that use a hybrid cloud can leverage the benefits of both public and private clouds.
One key advantage of using a hybrid cloud is that it can be configured so that it uses the public cloud for non-sensitive workloads that require scalability and it can be highly cost effective.
In addition, it can utilise the private cloud for sensitive workloads that require high levels of security and compliance.
A hybrid cloud offers companies the flexibility to utilise both private and public cloud services according to their needs.
For example, a company using a hybrid cloud model might choose to use public cloud services for non-sensitive workloads and data sharing between the employees of their business, but a private cloud for their more sensitive data and operations.
What are the benefits and disadvantages of a Private Cloud?
Here are some other common benefits of using a private cloud:
- Flexible & adaptable – Private clouds allow companies to adapt their digital space specifically to their needs.
- Safe & secure – Being a private digital space, no unauthorised persons or organisations have access, making it extremely secure.
- Security measures are customisable – Companies can tailor their security measures to follow specific protocols and configurations that are required for their operations.
- Greater performance – Private clouds can offer a greater level of performance as they are customised to the company’s needs.
- Total ownership of resources – Companies own their own cloud and don’t need to share them with other customers.
There are also some drawbacks to using a private cloud environment:
- Cost – Opting for a private cloud computing environment is expensive. Companies have to pay for all of the hardware, as well as the physical space to keep it in. It can take a long time to set up and certainly requires a significant financial investment initially.
- Maintenance – As well as setting up a private cloud, companies need to maintain it. This means hiring full-time IT security staff to monitor, develop and maintain the infrastructure.
- Scalability – While it is true that private clouds offer useful scalability options for companies, this takes time and planning. Private cloud infrastructures may have difficulties dealing with unpredictable spikes in traffic.
- Licences – These are required for private clouds and this can be expensive.
- Hardware – After a few years, the hardware is outdated and needs to be upgraded.
When to use a Private Cloud environment?
A private cloud environment is often used in the following circumstances:
- When companies deal with high levels of sensitive data.
- In industries and agencies that are highly regulated.
- For companies who need to have tight control over their IT infrastructure.
- For large companies who can afford to invest in their data centre capabilities in the interest of cost and efficiency.
What are the benefits and disadvantages of the Public Cloud?
Some key advantages of using the public cloud include:
- Cost – There are no initial cost investments required when setting up (compared to private clouds). Similarly, there is no ongoing cost of maintaining the IT infrastructure.
- Agility – Companies can scale up or down efficiently without the need to invest large amounts of money. This allows them to keep their operations agile and focus their financial resources on the development and innovation of their projects.
- Flexibility & affordability – The public cloud allows companies to opt for more services as and when they are required.
- Availability – There are many public cloud services to choose from which also offer different levels of availability (SLAs). This is beneficial to companies as they have a greater choice.
- Integration – It is generally a straightforward and uncomplicated process to integrate the public cloud into a business.
- Sustainability – Public clouds provide sustainable environments for businesses to use.
There are also various drawbacks that need to be considered when using a public cloud, including:
- Cost – While it can be cost effective to opt for a public cloud, it is important that there is strict financial management and governance in place to keep it viable, especially in larger environments.
- Security – Public cloud providers are known to the general public which unfortunately means that they are constantly exposed to risk in the form of hacks or leaks.
- Lack of physical control – Using a public cloud provider means that the company has absolutely no control of the infrastructure that they are using.
When to use a Public Cloud environment?
A public cloud environment is beneficial in the following circumstances:
- For all businesses who have good architecture design, where legislation doesn’t impede them.
- For companies who have ‘lower demand’ business needs that are constant.
- It can also be used by companies who have higher usage demands to help cope with increased traffic.
- As a ‘backup’ to a private cloud environment to help businesses deal with unexpected peak network demands.
- As a test environment for new software.
- If your company operates internationally over multiple countries or continents, a public cloud environment is very useful as you are able to replicate their services effectively in a different geographical location.
- For companies who operate with low latency times, the public cloud is an excellent option as it allows them to generate offers or manage high numbers of requests at a very quick speed.
- For companies who cannot afford the upfront cost of a private network, the public cloud is an excellent choice. It allows them to scale over time and spread the cost.
What are the benefits and disadvantages of a Hybrid Cloud?
Many companies that have made their digital transformation are now opting for the hybrid cloud model for a variety of reasons. Hybrid clouds offer greater flexibility, cost savings, and scalability compared to using only private or public clouds.
Here are some more common benefits of utilising the hybrid cloud:
- Security & control – Companies are able to develop their own private cloud environment while simultaneously having peace of mind that should something happen (e.g. a spike in traffic), they can fall back on the public cloud.
- Reliability – By distributing their IT services across a variety of private and public data centres, maximum reliability can be achieved.
- Cost – Companies can utilise their own private data centres to look after the ‘heavy lifting’ in terms of data usage while using the public cloud for operations that are less data-heavy.
- Overall efficiency – As the hybrid cloud model allows companies to pick and choose the most desirable attributes of both private and public models, they can achieve maximum time, cost and operation efficiency.
As effective as the hybrid cloud model is, there are some potential drawbacks to consider:
- Cost – While the hybrid model can offer huge benefits in cost optimisation, there is a risk that switching between public and private cloud models can be difficult to optimise and can result in inefficient spending if not monitored carefully.
- Control – While private cloud environments offer high degrees of control and oversight, public models don’t. This can be hard to balance for companies that may struggle with the lack of oversight that they have in specific areas of their operations.
- Complexity – Anytime more infrastructure is added to a company’s operations, it adds complexity. The extra time that it takes to understand and manage the systems means that errors can occur and inefficiencies can creep in.
When to use Hybrid Cloud environment?
A hybrid cloud environment is beneficial in the following circumstances:
- Companies that prefer to be highly strategic in their approach to cloud computing and are comfortable with maintaining a high level of insight and control.
- Companies with a wide range of regulatory, security and performance needs that can be met by a dynamic cloud environment.
- Businesses who are seeking to optimise their cloud investment without sacrificing the quality of their services or operations.
- Businesses that wish to use private clouds for highly sensitive data and public clouds for less sensitive data.
- During a transition period when a company is moving their operations.
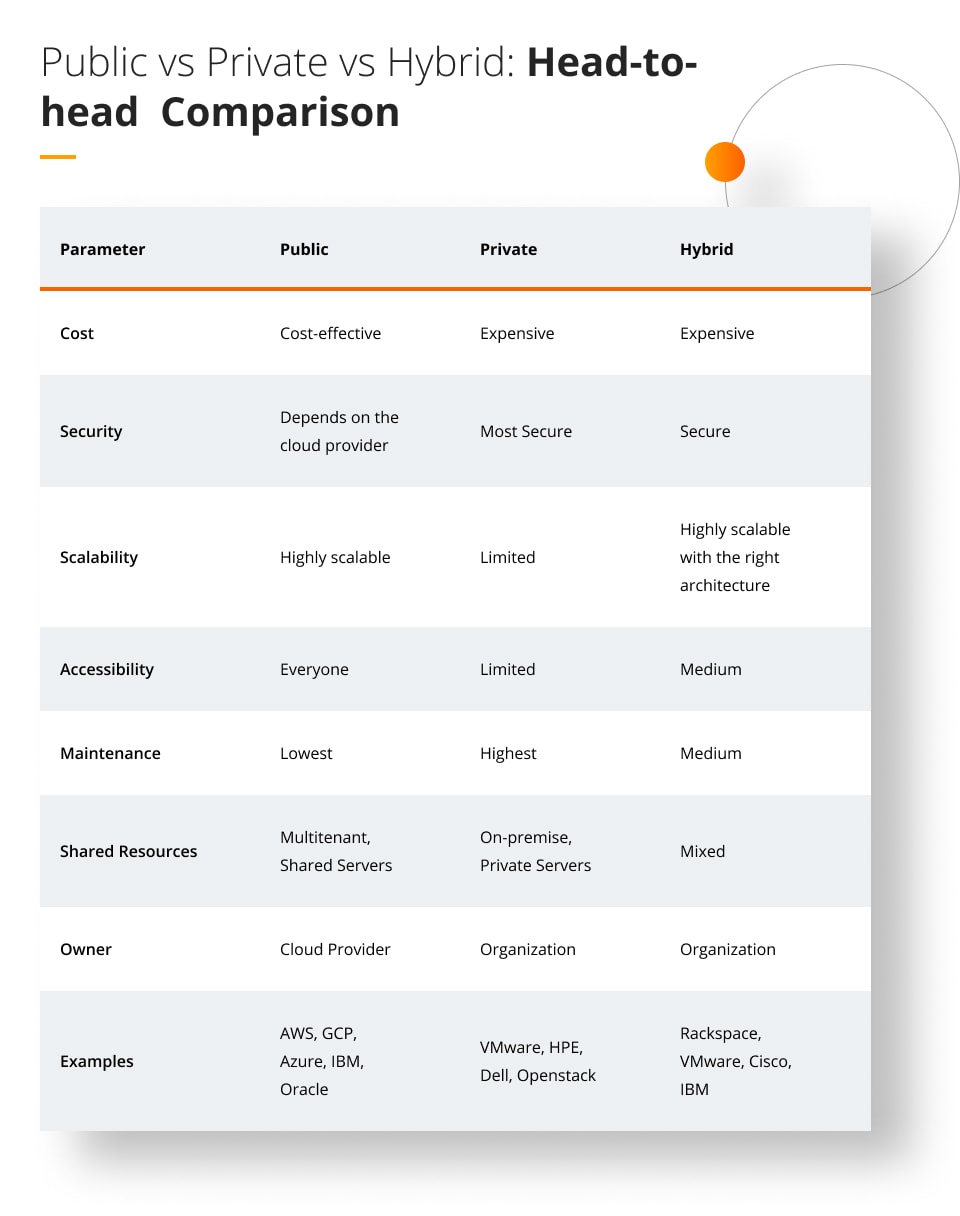
Which is better: the Private Cloud, Public Cloud or Hybrid Cloud?
Knowing which cloud environment to choose for your organisation can be tricky. It all depends on the size of your business, the nature of your operations, your budget, any physical constraints and your ability (or willingness) to maintain a cloud environment.
Typically, startups or smaller businesses will opt for public cloud services due to their low investment requirements and accessibility.
Whereas medium and larger-sized enterprises will likely go for either private cloud services or a hybrid model which combines the best of both private and public cloud services.
It’s important to note that it is impossible to say ‘public models are the best because…’, or ‘hybrid models are the ONLY viable solution…’ – at the end of the day, each company must make their own decision according to their business needs, financial or time constraints, and any relevant legislation.
Which cloud services should you choose?
Considering which cloud infrastructure to use can be difficult. There are many cloud computing services to choose from, and many companies opt for a cloud consulting service to assist them in their decision, which can be really useful.
Companies may choose private or public cloud services according to their needs, financing and initial setup priorities. When creating a hybrid cloud environment, any combination of public and private cloud services can be used, regardless of the size of each component.
Businesses may choose to go for a larger public cloud environment at the beginning of their operation, and then over time, slowly expand the private cloud environment according to their needs. This process could also be carried out the other way around.
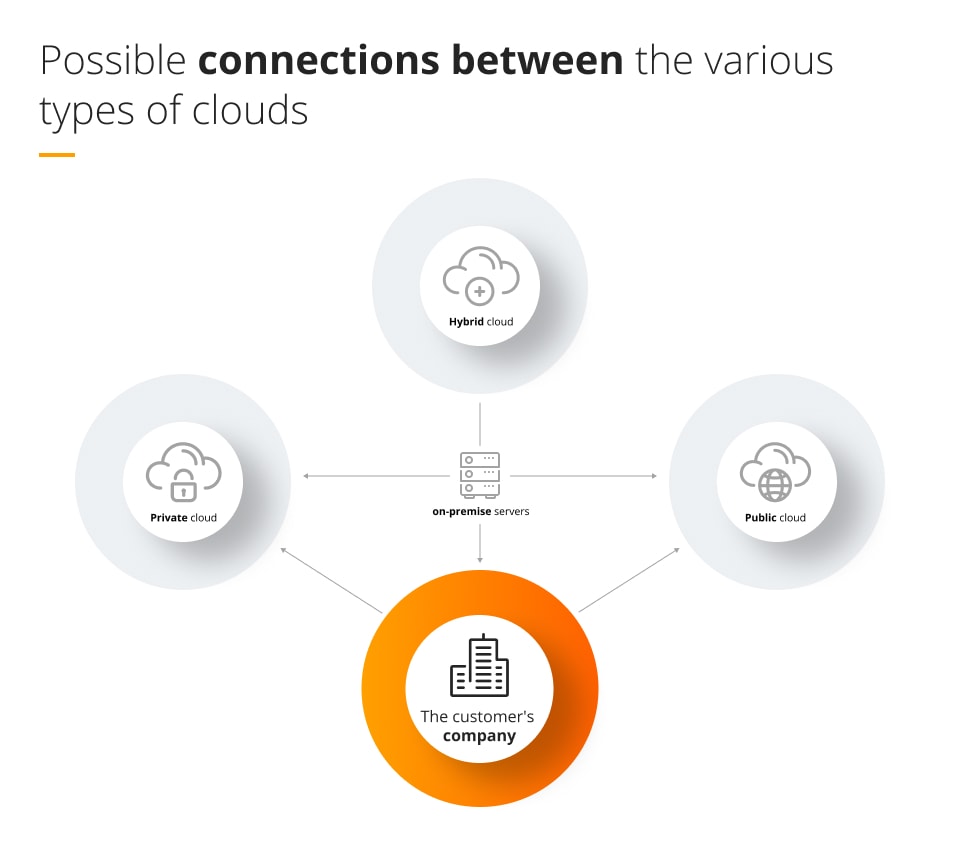
Have a look at the image below which shows the possible connections between the various types of clouds that companies could opt for.
Summary
Whether you are still yet to make your digital transformation over to the cloud or if you have already done so but are curious about optimising your cloud environments, it’s definitely worth creating a cloud strategy for your company.
This will help you to determine your needs, resources and financial capabilities and conclude whether a private, public or hybrid model is optimal for your business operations.