Insurance digital transformation: (r)evolution in the industry
Today we look at the insurance industry and how innovations transform it on a daily basis.
The ongoing digital transformation is changing the world and most industries are doing their best to keep up with those changes by introducing new technologies to serve their clients and improve their services.
What is digital transformation (DT)?
Before we look at the insurance industry in detail, let’s look for a moment at digital transformation.
Digital transformation encompasses various aspects, including technology adoption (AI, IoT), processes optimisation, enhancement of customer experience, data-driven decision making, organisational culture and change, as well as agile and flexible operations.
The goal of digital transformation is to create a digitally mature organisation that leverages technology to drive growth, improve competitiveness, and deliver value to stakeholders. It is a strategic on-going initiative that goes beyond implementing isolated digital solutions and requires a holistic approach that considers technology, processes, people, and culture.
Digital transformation in the insurance sector: from policies to pixels
Over the years, the insurance sector has undergone a significant digital transformation, shifting from traditional paper-based processes to digital platforms and technologies.
The first digitalisation efforts started in the 1980s and 1990s, when insurance companies began digitising their processes by adopting computer systems for policy management, claims processing, and customer data management. This marked the initial steps towards automating manual tasks and improving operational efficiency.
The next big step ahead happened in the late 1990s and early 2000s with the rise of the internet, when insurance companies started offering online platforms for customers to purchase policies directly. This shift allowed customers to compare plans, receive quotes, and complete transactions digitally, reducing the reliance on traditional agent-based sales.
With the increasing popularity of smartphones, insurance companies developed mobile applications to provide customers with convenient access to policy information, claims filing, and customer support. Today mobile apps enable policyholders to manage their policies, view coverage details, and file claims from their devices.
All of those processes happened over years and insurance companies were sometimes slow to adopt and embrace them. Yet the current digital transformation pushes them even further by unlocking new potential and giving access to new technologies in a more rapid way. Today, insurance companies use data analysis tools, telematics and usage-based insurance, all to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, improve risk assessment, and deliver a better customer experience. Insurers continue to explore emerging technologies and trends to stay competitive in a digitally-driven marketplace.
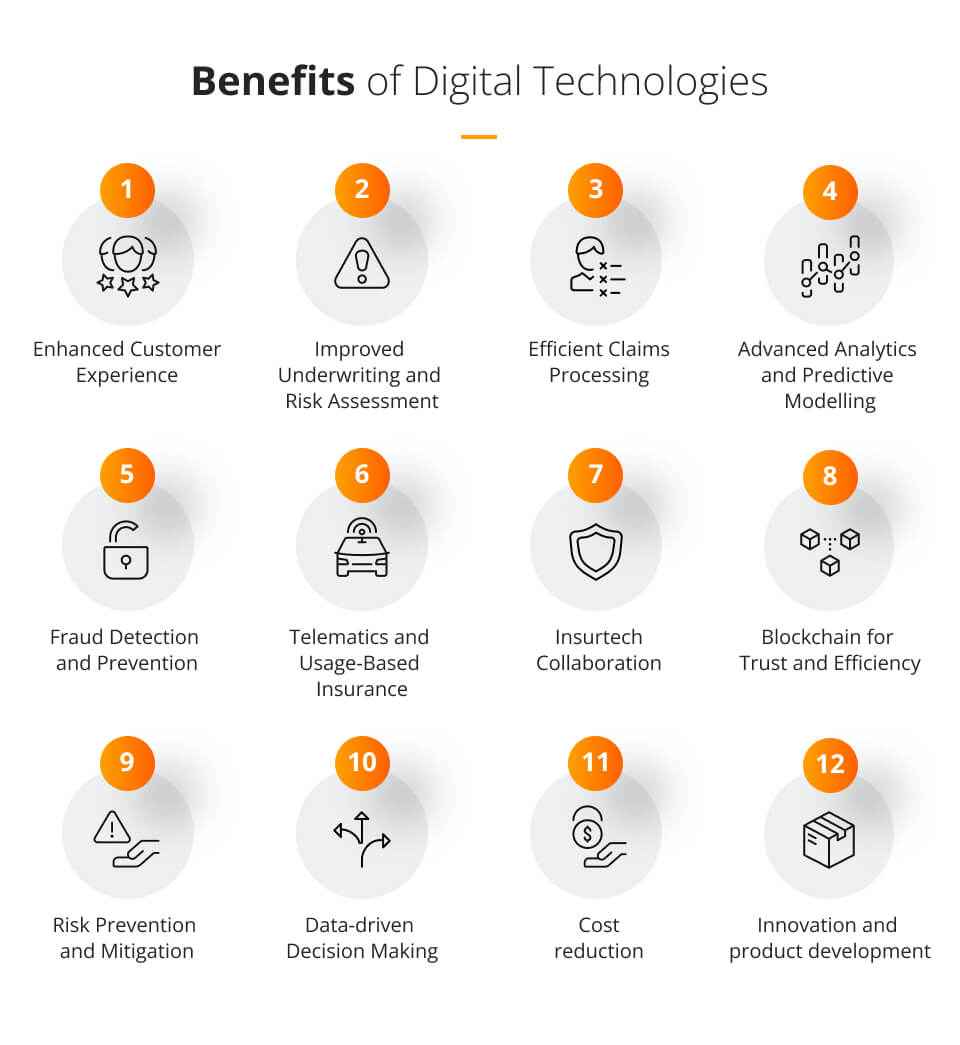
The potential and benefits of digital technologies in the insurance industry
Digital technologies have immense potential to transform the insurance industry and bring significant benefits for insurers, customers, and other stakeholders.
Some key areas where digital technologies can have a positive impact include:
1. Enhanced Customer Experience
Digital technologies enable insurers to offer a seamless and personalised customer experience. Insurers can leverage data analytics, AI-powered chatbots, and self-service portals to provide 24/7 customer support, faster policy issuance, convenient claims processing, and personalised product recommendations.
2. Improved Underwriting and Risk Assessment
Digital technologies allow insurers to gather and analyse vast amounts of data from various sources, including social media, wearables, and telematics. This data can be used to assess risks more accurately, develop personalised policies, and price premiums based on individual behaviour and usage patterns.
3. Efficient Claims Processing
Automation and digitisation streamline the claims process, reducing paperwork, manual interventions, and processing times. Technologies such as optical character recognition (OCR), image analysis, and automated workflows can expedite claims handling, improve accuracy, and reduce fraudulent claims.
4. Advanced Analytics and Predictive Modelling
Data analytics, machine learning, and predictive modelling help insurers gain valuable insights into customer behaviour, market trends, and risk patterns. These insights can drive more informed decision-making, enable proactive risk management, and support the development of innovative insurance products.
5. Fraud Detection and Prevention
Digital technologies enable insurers to implement advanced fraud detection systems. AI algorithms can analyse data patterns and detect anomalies that indicate potential fraudulent activities, helping insurers mitigate risks and protect themselves and their customers from fraudulent claims.
6. Telematics and Usage-Based Insurance
Telematics technology, including GPS and sensors, allows insurers to collect real-time data on driving behaviour, enabling usage-based insurance models. Insurers can offer personalised premiums based on actual usage, safe driving habits, and other factors, incentivising policyholders to adopt safer behaviours.
7. Insurtech Collaboration
Insurtech startups bring innovative technologies and ideas to the insurance industry. Collaboration between traditional insurers and insurtech companies can drive digital innovation, improve operational efficiency, and deliver new products and services that cater to evolving customer needs.
8. Blockchain for Trust and Efficiency
Blockchain technology offers transparency, security, and trust in insurance transactions. It can streamline processes such as claims settlement, contract management, and policy verification by providing a decentralised and immutable ledger that all parties can access and trust.
9. Risk Prevention and Mitigation
Digital technologies enable insurers to provide risk prevention and mitigation services to their customers. For example, insurers can partner with IoT device manufacturers to offer smart home security solutions or collaborate with health and wellness apps to promote healthier lifestyles and reduce healthcare risks.
10. Data-driven Decision Making
Digital technologies provide insurers with access to vast amounts of data, enabling data-driven decision-making across all areas of the business. Insights from data analytics help insurers identify market trends, optimise product portfolios, improve operational efficiency, and manage risks effectively.
11. Cost reduction
By minimising manual processes and eliminating paper-based workflows, insurers can significantly reduce administrative costs. Digital channels and self-service options also reduce the need for extensive agent networks, resulting in cost savings.
12. Innovation and product development
Insurers can leverage emerging technologies such as AI, IoT, blockchain, and data analytics to develop new products and services. These innovations may include usage-based insurance, on-demand coverage, digital platforms for policy comparison, and personalised offerings tailored to specific customer needs.
The potential of digital technologies in the insurance industry is vast and continually evolving. Insurers that embrace digital transformation and effectively harness these technologies can gain a competitive edge, deliver better customer experiences, and drive innovation in the insurance market.
The rise of insurtech: a new era for the insurance
The rise of Insurtech, which stands for insurance technology, has ushered in a new era for the insurance industry.
Here are some key aspects of the Insurtech movement:
Innovation in product offerings
Insurtech startups have introduced innovative insurance products and services that cater to changing customer needs and preferences. These products often leverage emerging technologies such as AI, IoT, blockchain, and data analytics to provide more personalised coverage, on-demand policies, and usage-based insurance options.
Improved customer experience
Insurtech companies prioritise delivering a seamless and user-friendly customer experience. They leverage digital platforms, mobile apps, and self-service portals to simplify the insurance process, enable easy policy management, offer transparent pricing, and provide quick and efficient claims processing. Insurtech firms often emphasise customer-centricity and aim to engage customers through intuitive interfaces and personalised interactions.
Data analytics and risk assessment
Insurtech companies leverage advanced data analytics techniques to gather, analyse, and interpret large volumes of data from various sources. This enables them to assess risks more accurately, develop innovative underwriting models, and provide personalised pricing based on individual behaviour and usage patterns. Insurtech firms often rely on real-time data and predictive analytics to enhance risk assessment and mitigation strategies.
Automation and operational efficiency
Insurtech startups leverage automation technologies to streamline and digitise insurance processes, eliminating manual paperwork and reducing administrative burdens. Robotic process automation (RPA) and AI-powered chatbots are used for tasks like policy issuance, claims processing, customer support, and data entry. This automation enhances operational efficiency, reduces costs, and allows employees to focus on higher-value activities.
Insurtech ecosystems and partnerships
Insurtech companies often collaborate with traditional insurance carriers, technology firms, and other players in the insurance ecosystem. These partnerships facilitate knowledge sharing, access to resources, and the integration of innovative technologies. Insurtech startups also collaborate with data providers, IoT device manufacturers, and other industry stakeholders to access relevant data sources and enhance their offerings.
Disruption and market competition
Insurtech has introduced competition and disruption to the traditional insurance landscape. Insurtech startups are challenging established players with their agility, customer-centric approach, and innovative business models. This has led to increased market competition, prompting traditional insurers to embrace digital transformation and explore partnerships or investments in Insurtech ventures.
Insurtech regulatory environment
Regulators are adapting to the evolving Insurtech landscape by introducing frameworks and guidelines to address regulatory challenges and ensure consumer protection. Regulatory sandboxes, which provide a controlled environment for testing innovative insurance solutions, have emerged in several jurisdictions, allowing Insurtech firms to experiment with their products and services within defined regulatory boundaries.
Open insurance and API integration
Insurtech promotes the concept of open insurance, encouraging the use of application programming interfaces (APIs) to enable seamless integration and collaboration between insurance companies, Insurtech startups, and other digital platforms. This allows for data sharing, faster product development, and enhanced customer experiences through integrated services.
The rise of Insurtech has brought forth a wave of innovation and digital transformation in the insurance industry. Traditional insurers are increasingly adopting Insurtech practices and partnering with Insurtech startups to stay competitive in the evolving digital landscape. The continued growth of Insurtech is expected to shape the future of insurance, driving customer-centricity, operational efficiency, and technological advancements.
Challenges of digitalisation in insurance
While digitalisation brings numerous benefits to the insurance industry, it also presents several challenges that insurers must navigate. The key ones include:
- Legacy systems and infrastructure – many insurance companies have complex legacy systems and infrastructure that may not be compatible with modern digital technologies. Upgrading or integrating these systems is a challenging operation that requires time, effort, and great planning. Legacy systems can hinder the agility and flexibility required for effective digital transformation.
- Data management and privacy – digitalisation generates vast amounts of data, and insurers must effectively manage, store, and secure this data. Ensuring data privacy and compliance with regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), is crucial. Data breaches and mishandling of customer data can damage an insurer’s reputation and result in legal and financial consequences.
- Change management and workforce adaptability – implementing digital transformation requires a cultural shift within the organisation and the adaptation of employees to new processes and technologies. Resistance to change and lack of digital skills can impede successful digitalisation efforts. Insurers need to invest in change management strategies, training programs, and hiring or upskilling employees with digital competencies.
- Cybersecurity risks – as insurers adopt digital technologies, they become more vulnerable to cyber threats. Cyberattacks, data breaches, and ransomware attacks can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and customer distrust. To mitigate these risks insurance companies should invest in cybersecurity measures and think about them as an inseparable part of their operations.
- Customer expectations and experience – digitalisation, while improving customer experience, also raises expectations. Today customers expect seamless digital interactions, personalised services, and real-time access to information. Meeting these expectations requires insurers to invest in user-friendly interfaces, omnichannel capabilities, and responsive customer support. Failing to deliver a satisfactory digital experience can lead to customer churn.
- Regulatory and compliance requirements – insurance is a highly regulated industry, and digitalisation adds complexity to compliance efforts. Insurers must navigate regulatory frameworks and ensure that digital processes comply with legal requirements. Staying abreast of regulatory changes and adapting digital systems accordingly can be challenging.
- Integration and collaboration – digitalisation often involves integrating various systems, platforms, and data sources. Insurers may face challenges when integrating with external partners, such as Insurtech startups, third-party vendors, or data providers. Ensuring seamless data exchange, interoperability, and maintaining security standards across these integrations is a complex and challenging task, which should be undertaken carefully and with expertise by experienced professionals.
- Overcoming industry inertia – the insurance industry, known for its traditional practices and risk-averse nature, can be resistant to change. Encouraging widespread adoption of digital transformation initiatives and driving innovation may require overcoming organisational inertia, aligning stakeholders, and fostering a culture of innovation within the industry.
While these challenges exist, they can be mitigated through careful planning, investment in technology and infrastructure, collaboration with insurtech partners, effective change management, and prioritising cybersecurity and data privacy. Successful digitalisation efforts require a holistic approach that addresses these challenges while keeping customer needs and market trends in focus.
Companies that went through successful insurance transformation: examples
Several companies in the insurance industry have successfully undergone digital transformation to stay competitive and deliver innovative solutions. Here are a few examples:
- AXA – a multinational insurance company that has embarked on a digital transformation journey to enhance its customer experience and operational efficiency. It has developed digital platforms and mobile apps to enable customers to manage policies, file claims, and access insurance services. AXA has also partnered with Insurtech startups and invested in digital innovation labs to drive new ideas and technologies. Its separate division, AXA XL, embrace usage of new technologies and platforms.
- Allianz – one of the largest insurance companies globally that has embraced digitalisation to enhance its customer offerings and improve operational efficiency. It has invested in digital platforms, data analytics, and automation to streamline underwriting, claims processing, and customer interactions. Allianz has also explored emerging technologies such as blockchain for secure and transparent transactions.
- Zurich Insurance has undergone digital transformation to strengthen its market position and improve customer engagement. It has adopted digital platforms and automation tools for policy administration, claims processing, and risk assessment. Zurich Insurance also collaborates with Insurtech startups through its innovation lab, seeking new technologies and business models to drive innovation.
These companies serve as examples of successful digital transformation in the insurance industry. They have leveraged technology, embraced innovation, and prioritised customer-centric approaches to thrive in the digital era. Their experiences demonstrate the potential for traditional insurers to adapt and evolve by harnessing the power of digital technologies and embracing a customer-first mindset.
The future of insurance: trends shaping the digital transformation
The future of insurance is being shaped by several key trends that are driving the digital transformation of the industry. These trends are reshaping the way insurance products are developed, distributed, and serviced, and they have a significant impact on customer expectations and the overall insurance landscape.
1. Personalisation and Customisation
Customers increasingly expect personalised insurance products that cater to their unique needs and circumstances. Digital technologies enable insurers to gather and analyse vast amounts of data to offer personalised coverage, pricing, and risk management solutions. Insurers are leveraging technologies such as data analytics, AI, and machine learning to assess risks, create tailored policies, and provide personalized recommendations and services.
2. Usage-Based Insurance
Usage-based insurance (UBI) is gaining popularity as insurers leverage telematics, IoT devices, and other data sources to assess risks based on actual usage patterns. UBI allows for more accurate risk assessment and pricing, as premiums are determined by the individual’s behaviour, driving habits, or usage of insured assets. This trend promotes fairness, encourages safer behaviour, and enhances customer engagement.
3. Insurtech and Collaboration
Insurtech startups continue to disrupt the insurance industry by introducing innovative business models, technologies, and customer-centric solutions. Collaboration between traditional insurers and Insurtech companies is becoming more prevalent, allowing insurers to tap into the agility and technological expertise of startups. Partnerships and investments in Insurtech ventures enable traditional insurers to accelerate their digital transformation efforts and drive innovation.
4. Digital Platforms and Ecosystems
Digital platforms are playing a significant role in reshaping insurance distribution and customer interactions. Insurers are leveraging digital platforms to offer self-service options, enable seamless policy management, and provide value-added services beyond traditional insurance coverage. Additionally, insurance ecosystems are emerging, where insurers collaborate with other industry players, such as Insurtech startups, healthcare providers, and technology companies, to offer integrated and comprehensive solutions to customers.
5. Customer Experience and Engagement
Customer expectations are evolving, and insurers are focusing on enhancing the overall customer experience. Digital technologies enable insurers to offer user-friendly interfaces, personalised interactions, and convenient self-service options. Insurers are investing in customer-centric digital strategies, including mobile apps, chatbots, and AI-powered virtual assistants, to provide quick responses, streamline processes, and deliver personalised recommendations and services.
6. Advanced Analytics and AI
Data analytics and AI play a crucial role in the future of insurance. Insurers are using advanced analytics to gain insights from large volumes of data, identify patterns, and make data-driven decisions. AI-powered algorithms are being deployed for various tasks, including underwriting, claims processing, fraud detection, and customer service. These technologies improve efficiency, accuracy, and speed, while also enabling insurers to offer proactive risk management and personalised experiences.
7. Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
With the increasing reliance on digital technologies and the growing threat of cyberattacks, cybersecurity and data privacy are critical concerns for insurers. The future of insurance requires robust security measures, proactive risk management, and compliance with data protection regulations. Insurers must invest in cybersecurity technologies, conduct regular audits, and prioritise data privacy to build trust with customers and protect sensitive information.
8. On-demand insurance for gig economy
Traditional insurance products often did not adequately address the specific needs of gig workers (those with temporary or freelance work arrangements) which led to the emergence of Insurtech companies aiming to offer more flexible and tailored insurance solutions, cost-effective and allowing the specific clients to find peace of mind.
9. Parametric insurance
Parametric insurance is a type of coverage that automatically pays out a predetermined amount based on a specific event or parameter, rather than traditional indemnity-based insurance which reimburses the actual loss incurred. This approach also proves to be time-efficient and flexible.
These trends highlight the transformative impact of digital technologies on the insurance industry. To stay competitive and meet evolving customer expectations, insurers need to embrace these trends, invest in digital capabilities, and foster a culture of innovation. The future of insurance lies in leveraging technology to create personalised experiences, offer tailored products, and build customer-centric ecosystems that go beyond traditional insurance coverage.
Digital transformation strategy: the roadmap for improvement
Developing a comprehensive digital transformation strategy is crucial for organisations aiming to improve their operations, enhance customer experiences, and stay competitive in the digital age. Such a strategy should contain clearly defined visions and objectives, prioritisation of areas of transformation, a roadmap that outlines the steps and timeline, as well as the plan for monitoring the project and communication about it across the organisation. Remember that digital transformation is not a one-time event, but an ongoing journey. It requires commitment, flexibility, and a willingness to embrace change.
A great way of starting your digital transformation process is to collaborate with an external partner, experienced in working with insurance companies keen to embrace this new world of innovation. Our team at Future Processing is delivering such projects for high profile organisations within insurance industry, so we will be happy to look into your case and help you make the most of digital transformation!