Artificial intelligence usage in multi-factor authentication
In today's technologically advanced world, securing sensitive information and protecting digital identities is paramount. Multi-factor authentication has emerged as a robust solution to improve security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification.
With the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence, it has become a game-changer in MFA, revolutionizing the way secure authentication processes are performed.
In this article, we will explore the various applications of AI usage in multi-factor authentication and delve into the benefits it brings to both businesses and users alike.
What is multi-factor authentication?
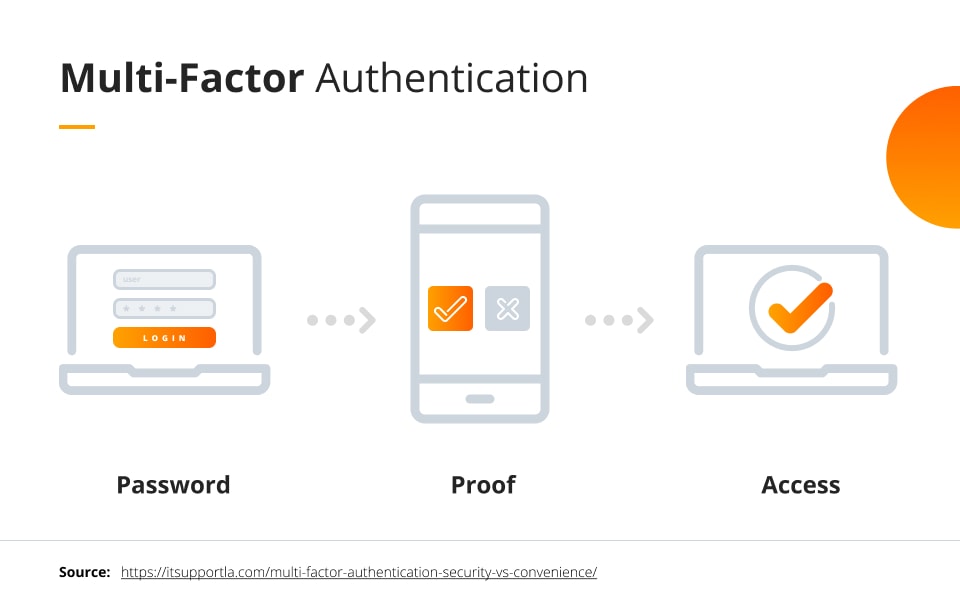
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), also known as two-factor authentication, is a powerful security enhancement that reinforces the protection of your digital online accounts. By requiring 2+ different forms of credentials during a login attempt, MFA significantly bolsters security. These credentials fall into three categories: something you know (e.g., password or PIN), something you have (e.g., smart card), or something you are (e.g., fingerprint). To ensure heightened security, the credentials must be from two distinct categories, making two different passwords insufficient for a multi-factor authentication process.
While the term MFA might be relatively new, its application has been prevalent in the financial industry for decades. Consider the last time you made a purchase using your bank card. You were prompted to provide both a physical item (your bank card) and specific information (your PIN). This dual-layered security protects you, as even if someone obtains your card, they would not possess your PIN. Such data security is necessary when finances are at stake. However, how does MFA enhance overall security? Let’s explore this from a hacker’s perspective.
Understanding the Resilience of MFA Against Hacking
To grasp the significance of MFA in safeguarding against hacking attempts, we must evaluate the risks and rewards that hackers and criminals face. With countless potential targets, hackers encounter varying levels of difficulty in their endeavors. While financial institutions, with their substantial investments in cybersecurity, pose significant challenges for hackers, smaller companies may appear more vulnerable.
If your organization relies solely on traditional, single-factor authentication, it becomes an easier target for criminals and fraudsters to work towards sensitive digital data. In essence, your company presents a more accessible opportunity for cyberattacks. Conversely, companies implementing MFA create additional obstacles for hackers, requiring them to acquire physical cards or devise strategies to manipulate biometric systems. In a world brimming with potential targets, only the most skilled attackers will invest their efforts in breaching well-protected organizations.
How AI is Improving Multi-factor Authentication Security
While multi-factor authentication is a strong defense in preventing unauthorized access, artificial intelligence advancements can add more layers of security.
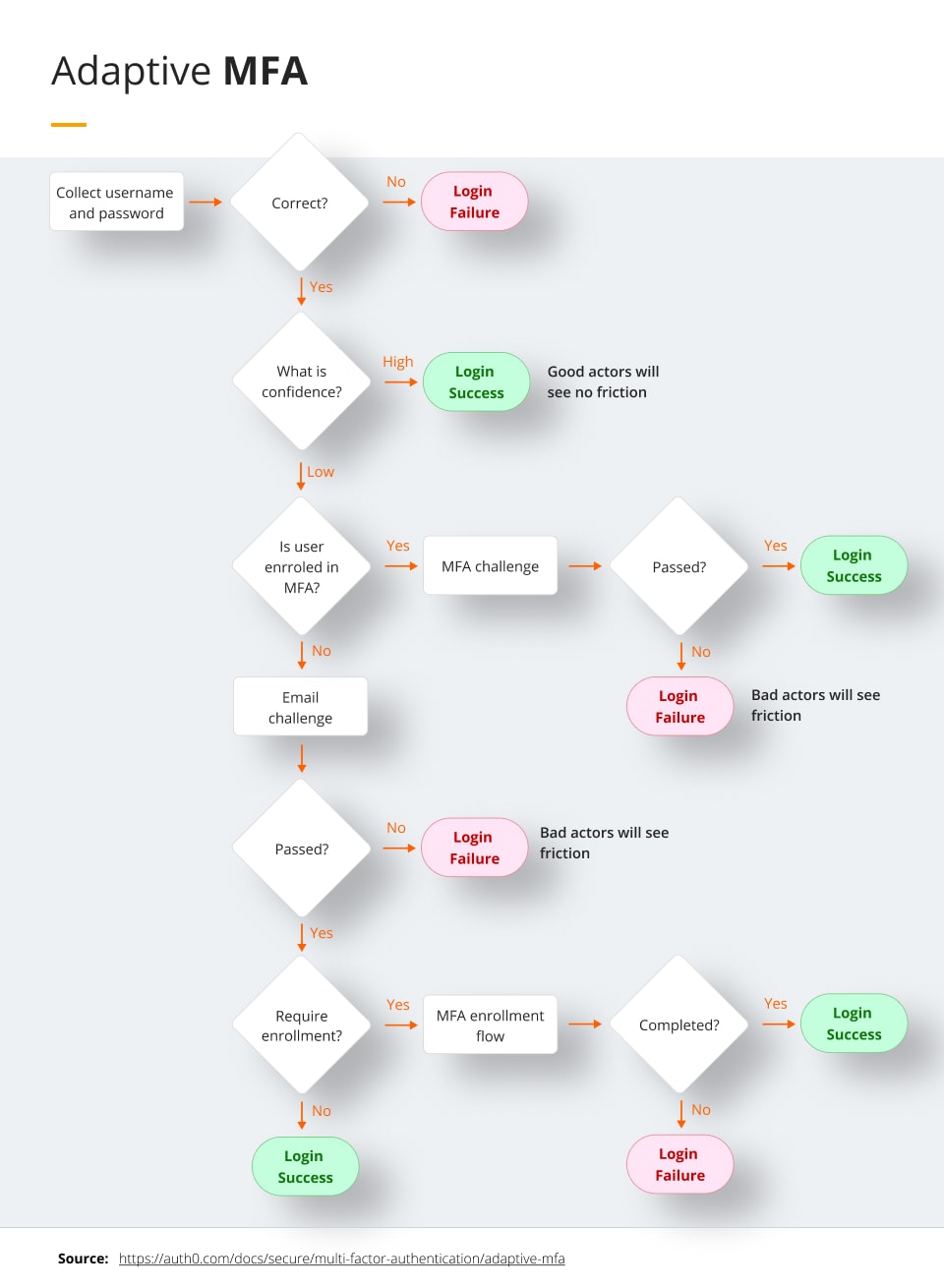
Adaptive MFA
Adaptive MFA uses contextual data to calculate the risk of the user’s login and choose a method of user authentication based on it. The risk is calculated based on different types of information, like location or IP address. For example, if someone is logging in from two different locations, the AI may get suspicious and require additional authentication before they can log in.
Along with requiring more authentication, the AI systems can warn the user of any suspicious activity that happens on their account. For example, if the system senses a login attempt from a new IP address, it may text the phone number linked to the same IP address the user has been confirmed to use before. The original user can then change their login information or ignore the warning if it is them.
Biometric Authentication with Machine Learning
Biometric authentication uses AI and deep learning techniques to confirm a user’s identity using biometric information, or physical characteristics. This can include fingerprint, iris, palm, or face recognition that uses deep learning, classification algorithms, or neural networks to verify biometric information. Using biometric authentication in conjunction with traditional authentication, like passwords, leads to a more secure MFA solution. However, it’s essential to recognize that the use of biometrics also brings inherent risks, as highlighted by the UE AI Act’s limitations and regulations pertaining to biometric data handling.
Risk-based authentication: the importance of continuous risk assessment
Risk-Based Authentication (RBA) is a security approach that uses AI and machine learning algorithms to assess the risk associated with a specific authentication request or session and then applies different levels of access or authentication requirements accordingly. Ongoing assessment is essential for RBA to be effective, as the risk associated with a user or device can change over time.
For example, an RBA system might consider the following factors when assessing the risk of an authentication request:
- The user’s location
- The device they are using
- The time of day
- The type of authentication request
- The user’s previous login history
- Based on this assessment, the RBA system might require the user to provide additional authentication factors, such as a one-time password or a fingerprint scan.
Ongoing assessment is important because the risk associated with a user or device can change over time. For example, if a user’s device is infected with malware, the risk of a successful attack increases. Similarly, if a user’s password is compromised, the risk of unauthorized access also increases.
Case Study: IBM Security Verify
IBM, one of the world’s largest IT companies, implements adaptive access and biometric authentication in their identity access management solution IBM Security Verify. It uses AI-informed risk scores to apply different levels of access, with a specialized risk-based authentication to higher-risk users. These high-risk events are also monitored and investigated for potentially dangerous user behavior to diagnose problems.
The first step in the IBM Security Verify process is verifying the user’s identity. Along with the traditional username and password authentication, it can check other variables and compare them with the verified user. These variables can include the user’s biometric information, login geography, MAC address, mouse speed, typing speed, device usage, and online behavior.
If this information is suspicious, it triggers a multi-factor authentication challenge, such as verifying login via SMS. While there are multiple methods to steal someone’s login information to impersonate them, it is harder for them to steal their phone for SMS verification, leading to more security.
IBM clients
Due to its AI-enhanced security features, IBM Security Verify has multiple high-profile clients, ranging from the data analytics company SAS to the oral health company Colgate. Most of the companies using it are from the US or Canada, and a majority of the companies are large (>$1000M). It is worth noting that IBM Security Verify still has a small market share when compared to other big companies like Google Identity Platform.
Challenges in multi-factor authentication AI implementation
In 2023, businesses embarking on the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA) solutions for organizational applications, such as Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD), may encounter various challenges. These challenges can differ from one business to another, but there are several common hurdles to be aware of.
One of the most prevalent challenges is user adoption. Some employees may be resistant to change, finding MFA solutions too complex or inconvenient to adopt. This reluctance can hinder the successful implementation and usage of MFA within the organization.
Another challenge is the lack of trust among employees. MFA solutions often require access to personal information like phone numbers and fingerprints for identity verification. Concerns over privacy and sensitive data security may lead some employees to be hesitant in providing sensitive information, thereby impacting their compliance with MFA requirements.
Time and cost constraints are also significant challenges. Initially, the implementation process can be time-consuming, requiring ongoing adjustments to align with business requirements. Businesses must invest resources, including time and money, to ensure the effective functioning of MFA, which may pose challenges, especially for organizations with limited resources.
Technical complexity is another obstacle, particularly for businesses that lack expertise in network security and identity and access management (IAM). Executing MFA solutions may necessitate specialized knowledge and skills, leading some businesses to consider hiring or consulting experts to overcome this challenge.
For organizations with legacy application systems, MFA can be particularly challenging. Legacy systems may not support modern authentication methods, requiring extensive system overhauls or code rewrites to ensure MFA implementation.
Simultaneous deployment of MFA across all organizational applications and resources is the ultimate goal. However, this can be challenging as network teams may lack familiarity and expertise in executing MFA protocols consistently across all resources.
While SMS authentication is a commonly used method for authentication and verification, its implementation can pose challenges. SMS-based protocols are vulnerable to cyberattacks and can make the entire network exploitable, potentially leading to data breaches. Finding alternative authentication methods that offer higher security levels may be necessary.
During the implementation process, businesses may realize that their MFA requirements extend beyond their initial expectations. Identifying and addressing these organizational needs can be challenging, potentially resulting in additional expenses and adjustments to the implementation plan.
Addressing Multi-factor Authentication Challenges
To address these MFA challenges effectively, businesses can adopt several strategies:
- Educating users: Businesses should focus on educating employees about the benefits and importance of MFA to build familiarity, trust, and understanding.
- Planning needs: Conducting a thorough analysis of the network infrastructure is crucial to identify the assets that require MFA security. This planning phase helps align MFA implementation with organizational requirements.
- Reviewing MFA solutions: It is essential to carefully examine and evaluate various MFA solutions to ensure they align with the organization’s capabilities and objectives.
- Identifying high-priority assets: Network teams should prioritize the deployment of MFA based on the importance and criticality of organizational assets. This approach ensures that the most valuable and sensitive resources receive the highest level of security.
- Using conditional access: Pairing MFA solutions with Azure Active Directory (AD) allows businesses to deploy condition-based access policies across organizational resources. This enhances security by granting access only under specific conditions or criteria.
- Monitoring performance: Once MFA solutions are deployed, businesses must continuously monitor their performance to identify any issues or areas for improvement. Regular evaluation helps in making necessary adjustments and optimizing the MFA solution for maximum effectiveness.
- Legislation: The EU AI Act is a comprehensive piece of legislation that aims to regulate the development and use of artificial intelligence (AI) in the European Union. The Act is still under development, but it is expected to have a significant impact on the use of AI in a wide range of applications, including multi-factor authentication (MFA). In addition to the challenges and limitations posed by the AI Act itself, there are also some general challenges and limitations associated with the use of AI in MFA. These include:
- Bias: AI systems can be biased, which could lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes in MFA. For example, an AI-powered MFA system that is trained on a dataset of users from a particular region or demographic group may be less accurate at authenticating users from other regions or demographic groups.
- Cost: Developing and deploying AI-powered MFA solutions can be expensive, which could limit their adoption by smaller organizations.
Despite these challenges and limitations, AI has the potential to significantly improve the security and usability of MFA. It is important to weigh the benefits and risks of using AI in MFA carefully, and to take steps to mitigate the potential risks.
By proactively addressing these MFA challenges and implementing these strategies, businesses can overcome obstacles, enhance security, and ensure the successful implementation and usage of MFA solutions within their organizations.
Conclusion
AI usage in multifactor authentication (MFA) has emerged as a powerful tool to bolster security measures and protect sensitive information. By leveraging AI technology, businesses can enhance the effectiveness and resilience of their MFA solutions, thereby mitigating potential risks and fortifying their digital identities.
Adaptive MFA, powered by AI, utilizes contextual data to calculate the risk associated with a user’s login attempt, enabling the system to dynamically choose the most appropriate method of authentication. This intelligent approach enhances security by requiring additional authentication steps for suspicious activities, providing an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
Biometric authentication, another artificial intelligence and machine learning driven application, leverages deep learning algorithms to verify users’ physical characteristics, such as fingerprints, iris patterns, palm prints, or facial features. By combining biometric authentication with traditional credentials, businesses can establish a highly secure MFA solution that significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
IBM Security Verify serves as a noteworthy case study showcasing the integration of AI in MFA. By utilizing AI-informed risk scores and adaptive access controls, IBM Security Verify applies varying levels of access based on risk assessments. This approach enables organizations to implement specialized risk-based authentication for higher-risk users, ensuring robust security measures are in place.
However, implementing AI-powered MFA solutions is not without its challenges. Businesses may face hurdles such as user adoption, lack of trust, time and cost constraints, technical complexity, legacy system compatibility, simultaneous deployment across resources, and the vulnerabilities associated with SMS authentication.
Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses educating users, planning infrastructure needs, reviewing MFA solutions, identifying high-priority assets, using conditional access policies, and monitoring performance.
By embracing these strategies and harnessing the potential of AI systems in MFA, businesses can overcome these challenges, strengthen their security posture, and ensure the successful implementation and utilization of multi-factor authentication solutions. With AI as a trusted ally, organizations can safeguard their digital assets, protect user identities, and foster a secure environment in today’s increasingly interconnected world.