How to develop a cybersecurity strategy in 6 steps?
This guide will help you develop an information security strategy tailored to your organisation's unique threats and needs so you can protect assets and data you can't afford to lose.
Today’s digital age has created an environment where cyber threats and technologies continually evolve, making cybersecurity an essential part of organisational resilience.
That’s why every company needs a solid cybersecurity strategy.
What is a cybersecurity strategy?
There is no longer room for doubt in today’s hyperconnected digital landscape:
An effective cybersecurity strategy safeguards digital assets from cyberattacks, protecting digital systems, networks, and data from unauthorised access, breaches, and damage.
Cybersecurity strategies include:
- A meticulous planning process that integrates policies, protocols, and technologies
- Risk mitigation and incident response
- Protecting sensitive information by ensuring its integrity, confidentiality, and availability
A cybersecurity strategy is a dynamic framework that evolves alongside the ever-changing cyber threat landscape, ensuring your organisation remains a solid fortress in the digital realm.
With a cybersecurity strategy, organisations can identify vulnerabilities proactively and confidently take preventative measures.
Why is a cybersecurity strategy important?
A robust cybersecurity strategy cannot be underestimated. A well-crafted cybersecurity strategy example acts as a proactive defence mechanism, preventing unauthorised access, data breaches, and cyber-attacks.
Organisations need cybersecurity strategies for several reasons:
- Safeguarding against cyber threats: A information security strategy provides a structured approach to defending against a wide range of cyber threats that target sensitive data, systems, and networks.
- Protecting sensitive information: By preventing unauthorised access and compromise, it ensures the integrity, confidentiality, and protection of critical information assets.
- Mitigating financial and reputational risks: A cybersecurity strategy reduces financial losses caused by data breaches, regulatory fines, and reputational damage.
- Ensuring business continuity: A robust strategy ensures productivity and customer trust by minimising disruptions caused by cyber incidents.
- Compliance adherence: It assures compliance with industry regulations and standards, legal requirements, and avoiding non-compliance penalties.
- Preserve customer trust: By demonstrating a commitment to safeguarding customers’ data and privacy, an information security strategy strengthens relationships and brand trust.
How do you develop a strong cybersecurity strategy?
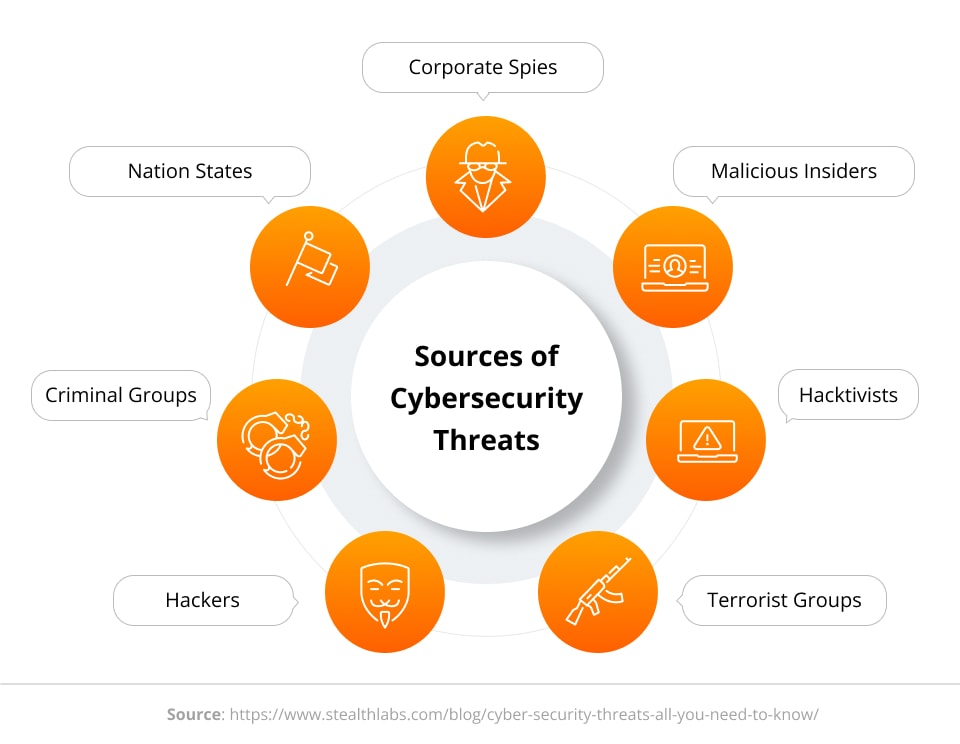
Step 1: Understand the cyber threats landscape
Developing an information security strategy requires awareness of the threats.
Understanding the multifaceted cyber threat landscape is the first step in building a strong cybersecurity strategy. This includes phishing attacks, malware attacks and sophisticated social engineering techniques.
Understanding adversaries’ tactics, techniques, and motives establishes the foundation for organisations to proactively strengthen their defences.
Threat intelligence assessments, including dark web monitoring, can help identify emerging risks. Comprehensive awareness of potential vulnerabilities across networks, systems, and data repositories is imperative.
It is also vital to remember about ensuring compliance with official regulations and directives, such as ISO27001, NIS 2.0, NIST, SOC2, GDPR, etc.
Step 2: Perform a cybersecurity risk assessment
Step 2 is a meticulous cybersecurity risk assessment. This evaluation involves assessing the likelihood and potential impact of various threats.
It also determines the assets at risk and prioritises mitigation efforts based on the risk levels identified. Conducting a comprehensive risk assessment allows organisations to evaluate existing security measures and identify potential weaknesses.
Cybersecurity risk assessment spans beyond technological facets, encompassing human factors and procedural loopholes.
Before devising a cybersecurity plan, proper risk identification and prioritisation of risks must be performed. This proactive approach allows organisations to preemptively fortify defences, directing resources strategically to mitigate high-risk areas.
Step 3: Design a comprehensive security policy
In the pursuit of a strong cybersecurity strategy, step 3 involves crafting a thorough and cohesive cybersecurity plan through a comprehensive security policy.
Developing a robust security policy entails establishing a clear set of guidelines, procedures, and protocols that govern security practices within an organisation.
This policy should encompass aspects like data encryption, access control, incident response plans and mechanisms, data handling procedures, employee training on security protocols, and employee responsibilities regarding cybersecurity.
This kind of policy acts as a guiding framework, delineating protocols, best practices, and compliance standards across the organisation. It must be designed to ensure alignment with emerging cyber challenges and organisational needs.
Step 4: Implement robust cybersecurity technologies and frameworks
Crafting a resilient information security strategy involves step 4: deploying robust cybersecurity technologies and frameworks.
Implementation begins with selecting cutting-edge technologies tailored to mitigate identified risks. This includes intrusion detection systems, encryption tools, next-gen firewalls, and AI-driven threat analytics.
Frameworks like Zero Trust Architecture, Secure Access Service Edge (SASE), NIST Cybersecurity Framework or ISO/IEC 27001 bolster the defence by emphasising continuous verification and least privilege access.
Integration of these technologies within a cohesive framework fortifies the security posture, ensuring a proactive defence against evolving cyber threats.
Step 5: Train and educate staff
Human error remains a significant factor in cyber incidents. That’s why step 5 in fortifying a security strategy involves training and educating staff comprehensively.
Educating and training employees on cybersecurity best practices including regular workshops, simulations of cyberattacks, and awareness programs can significantly reduce the likelihood of security breaches resulting from inadvertent actions or negligence.
A well-informed workforce serves as a vital line of defence against cyber threats. Continual education ensures staff remain abreast of evolving cyber threats and the latest security measures.
Step 6: Regularly review and update strategy
Cyber threats constantly evolve, making it imperative to review and adapt the cybersecurity strategy regularly. Thus, the last step in the cybersecurity plan is fortifying an information security strategy.
To keep continuous vigilance, organisations must mandate regular reviews and updates, conduct periodic assessments, revisit policies, update technologies, reassess threat landscapes, technology advancements, compliance standards, and incident response protocols and incorporate lessons learned from past incidents, which are vital in maintaining the efficacy of the cybersecurity strategy.
Regular review and updates to sustain resilience against evolving threats help identify gaps, emerging risks, and areas for enhancement within the security framework.
How to build a cybersecurity strategy for your business?
A comprehensive cybersecurity strategy example requires a proactive and holistic approach.
Implementing technology alone won’t suffice. Threats must be understood, risks assessed, personnel educated, and threats must be continuously adapted.
Following these steps and seeking the assistance of adept cybersecurity professionals like Future Processing can help businesses strengthen their cybersecurity defences and protect digital assets.
With Future Processing, you’ll have access to a comprehensive cyber strategy example suite, including:
- Cybersecurity consulting: we will assist you in identifying potential threats to your organisation and software product.
- Security Development Lifecycle: You’ll build more secure software by addressing security compliance requirements from the outset.
- Pentesting: The Future Processing team help you identify and resolve potential threats within your system, reducing data breach risk.
- Dependencies check and approved tools: Our experienced staff ensures your team uses only approved software.
- Application security testing and SecOps: Our experts will help you identify vulnerabilities that violate software development security practices.
- SIEM/SOC deployment: The team will gather system logs to detect unusual or suspicious activity. We monitor, investigate, and take action against cyber threats in real-time.
A robust cybersecurity strategy requires a multifaceted approach that seamlessly integrates technology, expertise, and continuous adaptation. An expert in cybersecurity can be a game-changer for a business looking to improve their digital security. Reach out if you would like to talk more about your cybersecurity strategy.